Sand casting process
Date: 2024-10-08 Categories: Blog Views: 3699
What is sand casting?
sand casting , also known as sand casting, is a time-honored method of casting process with a wide range of applications across the globe. It is a process method of producing castings by using clay-bonded sand (or sand molds made of other materials such as gypsum and silicone resin) as the molding material. The principle is to take advantage of the softness and ease of molding of the sand mold by pouring molten metal into the sand mold, and then crushing the sand mold after the metal has solidified in order to obtain the desired casting. Applied in a variety of metals, common aluminum sand casting, iron sand casting, copper sand casting, now give way to China'saluminumFoundryNingbo HexinThe sand casting process is explained in detail.

Sand casting production conventional process flow
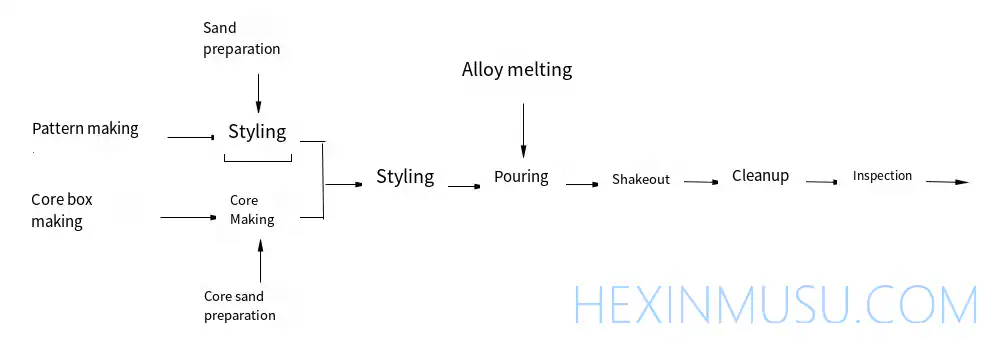
Sand casting process
(1) Preparation of molding sand and core sand
The molding materials used for sand casting are mainly sand used for making sand mold and core sand used for making sand core. Usually the sand is made of raw sand (mountain sand or river sand), clay and water mixed in a certain proportion, of which clay is about 9%, water is about 6%, the rest is raw sand. Sometimes a small amount of additives such as coal powder, vegetable oil, wood chips, etc. are added to improve the performance of the sand and core sand. The structure of the compacted sand is shown in the figure.
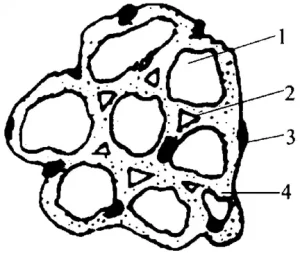
Schematic diagram of sand structure 1 - sand grains 2 - voids
3-Addition 4-Clay membrane
Core sand is generally prepared by hand due to its low demand.
The environment in which the core is harsh, so the core sand performance requirements than the high sand, while the core sand binder (clay, oil, etc.) than the binder in the sand in the ratio of the importance of some of the larger, so its permeability is not as good as the sand, the core should be made to make a breathable channel (holes); in order to improve the concessions of the core to be added to add additives, such as wood shavings.
Some demanding small castings tend to use oil sand core (tung oil + sand, baked until yellow-brown and become).
(2) Properties of molding sand
The quality of sand directly affects the quality of castings, poor sand quality will make sand casting products produce porosity, trachoma, sticky sand, sand and other defects. Good sand should have the following properties:
- ① Gas permeability The performance of the molding sand that allows gas to pass through is called gas permeability. High-temperature metal pouring into the casting, the type is filled with a large number of gases, these gases must be cast from the casting of the smooth discharge, otherwise the casting will produce porosity, underpouring and other defects. Cast air permeability by the sand particle size, clay content, moisture content and sand compactness and other factors. The finer the sand particle size, the higher the clay and moisture content, the higher the sand compactness, the worse the air permeability.
- ② Strength The ability of sand to resist external damage is called strength. The sand must have high enough strength in order not to cause collapse in the process of molding, handling, closing the box, and will not damage the surface of the casting when pouring. The strength of the sand should not be too high, otherwise the casting will be defective due to the decrease of air permeability and concessions.
- Refractoriness refers to the ability of the sand to resist high temperature and heat. If the refractoriness is poor, the casting is easy to produce sticky sand. The more SiO2 content in the sand, the larger the sand particles, the better the refractoriness.
- Plasticity refers to the ability of sand to deform under external force and to maintain the existing shape intact after removing the external force. Good plasticity, easy molding operation, accurate shape and clear contour of the sand mold.
- ⑤ Concession refers to the ability of the molded sand to be compressed when the casting is condensed. If the concessionality is not good, the casting is prone to internal stress or cracking. The tighter the sand, the worse the concessiveness. Adding wood chips to the sand can improve the concessiveness.
In a single piece of small batch production of sand casting product suppliers in the workshop, commonly used hand pinch method to roughly determine some of the properties of the sand, such as grabbing a handful of sand, tight pinch feel soft and easy to deform; let go of the sand after the mass is not loose, do not stick to the hand, and clear handprints; break it off, the section of the flat and even and no cracking phenomenon, and at the same time feel a certain degree of strength, it is believed that the sand has the appropriate performance requirements, the sand. As shown in the figure.
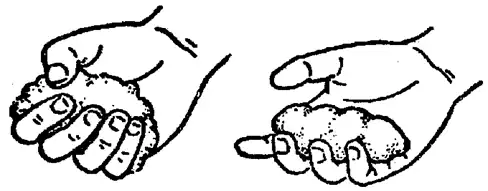
When the humidity of the sand is right, it can be seen when the hand is released.
It can be made into a sand ball by hand. Clear hand lines.
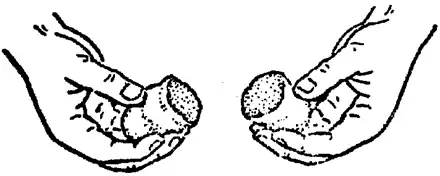
Fractured gap with fragmented shape when broken
At the same time there is enough strength
(3) Composition of molds
Moulds for sand casting products are made of molding material according to the shape of the part, and the moulds can be either sand or metal type. A sand mold is made from sand (core sand) as a modeling material. It is used for pouring metal liquid to obtain castings with the required shape, size and quality.
A mold generally consists of an upper mold, a lower mold, a core, a cavity and a pouring system, as shown in the figure to the right.
The joint surface between mold components is called the parting surface. The part of the cavity surrounded by the molding material in the casting, i.e. the cavity that forms the body of the casting, is called the cavity. Liquid metal flows into and fills the cavity through the pouring system, and the gas generated is discharged from the sand mold through the air outlet, etc. The mold is then filled with liquid metal.
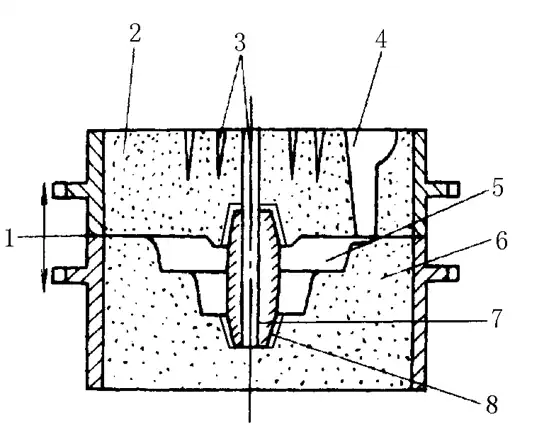
1-Molding surface 2-Upper mold 3-Vent 4-Pouring system 5-Cavity 6-Lower mold
7-core 8-core head holder
(4)Gating Systems
- Pouring System The pouring system is a series of channels in the mold for the liquid metal to flow into the cavity. Its function is to:
① Inject the metal fluid smoothly and quickly;
②Block slag, sand, etc. from entering the cavity;
③ Regulate the temperature of each part of the casting to supplement the volume contraction of the liquid metal during cooling and solidification.
Correctly setting the pouring system is of great significance to ensure the quality of castings and reduce the consumption of metal. If the pouring system is not reasonable, the castings are prone to defects such as sand blowing, sand holes, slag holes, failure to pour, porosity and shrinkage holes. Typical pouring system consists of four parts: outer gate, straight sprue, cross sprue and inner sprue, as shown in the figure below.
The cross sprue can be omitted for small castings with simple shapes.
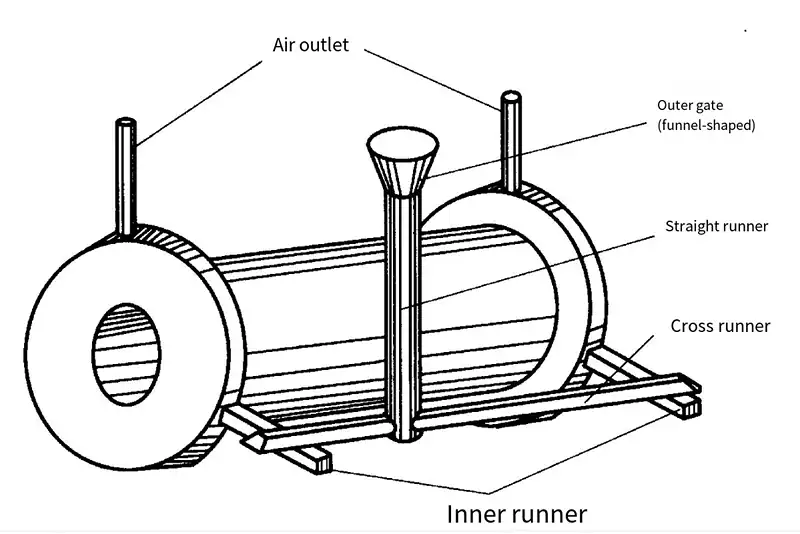
Typical casting systems
- ① Outer gate Its function is to contain the injected liquid metal and relieve the impact of liquid metal on the sand mold. Small castings are usually funnel-shaped (called gate cup), and larger castings are basin-shaped (called gate basin).
- ② Straight sprue It is a vertical channel that connects the outer gate with the horizontal sprue. Changing the height of the straight channel can change the static pressure of the liquid metal and change the flow speed of the liquid metal, thus changing the filling capacity of the liquid metal. If the height or diameter of the straight runner is too large, the casting will be underpoured. In order to make it easy to take out the rod, the straight channel is usually made into a conical shape with a big top and a small bottom.
- ③ Cross-channel It is a horizontal channel to introduce the metal liquid from the straight channel into the inner channel, which is generally opened on the parting surface of the sand mold, and its cross-section is generally high trapezoidal in shape and located on the top of the inner channel. The main function of the cross channel is to distribute the liquid metal into the inner channel and to block the slag.
- It is directly connected to the cavity and can regulate the direction and speed of liquid metal flow into the cavity and the cooling speed of each part of the casting. The cross-sectional shape of the inner sprue is generally flat trapezoidal and crescent-shaped, and can also be triangular.
- Risers Common defects such as shrinkage and loosening are caused by the volume contraction of the casting when it cools and solidifies. In order to prevent shrinkage and loosening, often in the casting of the top or thick part of the riser. Risers are the cavities and metal injected into the cavities in the casting. The liquid metal in the riser can constantly replenish the shrinkage of the casting, so that the casting can avoid shrinkage holes and shrinkage loosening. Risers are redundant and should be removed during cleaning. Risers in addition to supplement the role of shrinkage, but also the role of exhaust and slag collection.
(5) Manufacture of molds and core boxes
Mold is the necessary process equipment in the casting production. For castings with an internal cavity, casting the internal cavity formed by the sand core, and therefore also to prepare the core box for sand core. Manufacturing mold and core box commonly used materials are wood, metal and plastic. In a single piece, small batch production is widely used in wood mold and core box, in mass production more metal or plastic mold, core box. Metal mold and core box service life of up to 100,000 ~ 300,000 times, plastic service life of up to several tens of thousands of times, while the wooden only about 1,000 times. In order to ensure the quality of castings, in the design and manufacture of mold and core box, must first design the casting process map, and then according to the shape and size of the process map, manufacturing mold and core box. See the diagram below.
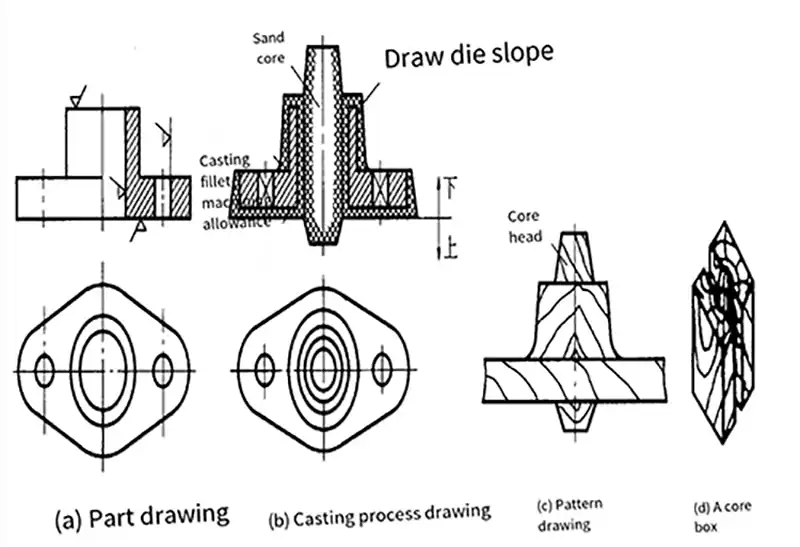
Here are some things to consider when designing a process map:
- ① Selection of parting surface The parting surface is the interface between the upper and lower sand molds, and the selection of the parting surface must enable the mold to be taken out of the sand mold and make the modeling convenient and conducive to ensuring the quality of the castings.
- ② Mold Pulling Slope In order to easily remove the mold from the sand mold, where perpendicular to the surface of the parting surface, are made 0.5º ~ 4º mold pulling slope.
- ③ Machining allowance The surface of the casting to be processed should be left with appropriate machining allowance.
- ④ Shrinkage The casting should shrink when cooling, and the size of the mold should take into account the influence of casting shrinkage. Usually used for cast iron parts to increase 1 percent; cast steel parts to increase 1.5 to 2 percent; aluminum alloy parts to increase 1 to 1.5 percent.
- ⑤ Casting rounded corner of the casting on the surface of the corner, should be made into transitional rounded corner, in order to facilitate modeling and ensure the quality of castings.
- (6) Core head For sand molds with a core, a corresponding core head must be made on the mold.
Styling Methods
The choice of modeling method should not only according to the type of production, but also according to the factory equipment conditions, casting size and complexity, as well as the quality requirements, to trace the integration of considerations. Molding methods can be divided into two categories of manual and machine molding.
Hand molding is mainly used for single-piece, small-lot production, while machine molding is mainly used for mass production.
(1). Hand modeling
- (A) The characteristics of complete molding are: the mold is a whole structure, the largest cross-section is flat at one end of the mold; the parting surface is mostly flat; and the operation is simple. The whole mold molding is suitable for castings with simple shapes, such as plates and covers.
- (B) The characteristics of split-mold molding are: the molds are separated, and the separated surface of the molds (called the parting surface) must be the largest cross-section of the molds, in order to facilitate mold starting. The process of split-mold molding is basically similar to that of whole-mold molding, but the difference is that the two operations of putting on the mold and taking the upper half-mold are added to the mold-making. Split molding is suitable for castings with complex shapes, such as sleeves, pipes and valve bodies.
- (C) live block molding molding on the removable or movable part called live block. When the mold on the side of the obstacle to the mold outstretched part (such as a small tab), the part is often made into a live block. When the mold, the mold body first removed, and then left in the casting of the live block alone, this method is known as the live block mold modeling. Nails connected to the live block molding, should pay attention to the first live block around the sand plug tight, and then pull out the nails.
- (D) sand molding when the casting according to the structural characteristics of the need for molding, but because of the conditions (such as mold is too thin, mold-making difficulties) is still made into a whole mold, in order to facilitate the mold, the lower parting surface needs to be dug into a curved surface or have a high and low changes in the shape of the ladder (called uneven parting surface), this method is called sand molding.
- (F) Three-box molding The process of manufacturing casting with three sand boxes is called three-box molding. Various molding methods mentioned above use two sand boxes, which are easy to operate and widely used. However, some castings, such as the two ends of the cross-section size is larger than the middle cross-section, you need to use three sandboxes, from the two directions respectively from the mold.
- (G) scraper molding size greater than 500mm rotating body castings, such as pulleys, flywheels, gears and other single production, in order to save wood, mold processing time and cost, can be used scraper molding. Scraper is a piece of wood board and casting cross-section shape. When molding, the scraper will rotate around the fixed center axis, and scrape the desired cavity in the sand mold.
- (H) Dummy box molding is the use of a prefabricated molding base plate or dummy box to replace the excavated sand in sand digging molding.
- (I) pit molding directly in the foundry sand or sand pit molding method is called pit molding. When large castings are produced in a single piece, pit molding is often used to save the sand box, reduce the casting height, and facilitate pouring operations. Pit molding structure, molding need to consider the pouring can smoothly lead the pit gas out of the ground, often coke, slag and other breathable materials bottom, and with iron pipe lead out of gas.
(2). Machine modeling
Manual molding productivity is low, the surface quality of castings is poor, requiring a high level of technical skills of workers, labor intensity, therefore, in mass production, are generally used in machine molding. Machine molding is the main operation of the molding process ---- tight sand and mold to achieve mechanization. According to the different ways of sand tightening and molding, there are pneumatic micro-vibration compaction molding, shooting pressure molding, high pressure molding, sand molding.
- (A) pneumatic micro-vibration compaction molding is used vibration (frequency 150 ~ 500 times / min, amplitude 25-80mm) - compaction - micro-vibration (frequency 700 ~ 1000 times / min, amplitude 5 ~ l0mm) compacted sand. l0mm) to compact the sand. This kind of molding machine has less noise, uniform compactness of sand and high productivity.
- (B) injection molding is characterized by the use of compressed air will be shot into the cavity sand for the initial compacting, and then the compaction piston will be compacted sand type again, sand type launched, before and after the contact surface between the two sand type for the parting surface. The casting size of injection molding is accurate, the surface roughness is small, and the productivity is high. It can produce 240-300 molds per hour, and is commonly used in the mass production of small and medium-sized castings.
- (C) High-pressure molding utilizes a hydraulic system to generate very high pressure to compact the sand mold. It is characterized by precise casting size, small surface roughness and high productivity. High-pressure molding is suitable for small and medium-sized castings with more complex shapes, multiple varieties, and production of medium batches or more.
- (D) Sand blasting molding is the use of high-speed rotating blades will be conveyed by the conveyor belt conveyor sand thrown down at high speed to tighten the sand mold. Sand throwing molding is highly adaptable, does not require special sand box and template, suitable for large castings of single piece of small batch production.
coring
In order to obtain the inner cavity or local shape of the casting, made of core sand or other materials, placed in the cavity inside the casting elements called core. The vast majority of cores are made of core sand. The quality of the core mainly depends on the preparation of qualified core sand and the use of correct core-making process to ensure.
When casting the sand core by the impact of high temperature liquid metal and surrounded, so in addition to the requirements of the sand core with the casting of the corresponding shape of the inner cavity, should also have a better permeability, refractoriness, concessions, strength and other properties, it is necessary to choose the quartz sand with few impurities and vegetable oil, water glass and other binders to formulate the core sand, and in the sand core put into the core of the metal core bone and tie up the ventilation holes in order to improve the strength and permeability.
Large and medium-sized cores with simple shapes can be manufactured with clay sand. However, for cores with complex shapes and high performance requirements, special binders must be used to formulate them, such as the use of oil sand, synthetic fat sand and resin sand.
In addition, the core sand should also have some special properties, such as low hygroscopicity (in order to prevent the core from returning to moisture after closing the box); less gassing (after the metal is poured, the core material should produce as little gas as possible when it is heated); and good sanding (in order to facilitate the removal of the core during cleaning).
The core is generally made of core box, and its open core box core making is a commonly used manual core making method, which is suitable for more complex cores with round cross section.
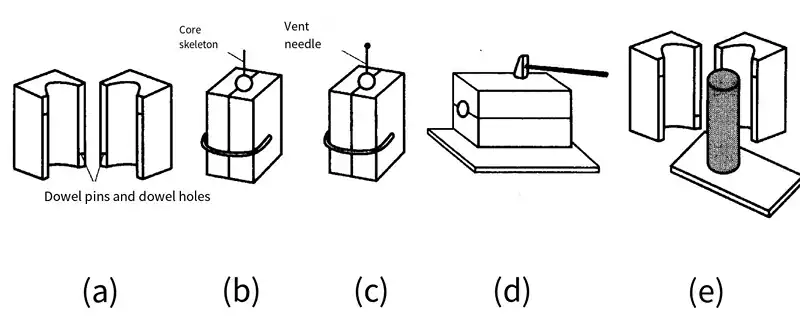
Folio core box core making
(a) Prepare the core box (b) Clamp the core box, add core sand and core bone in turn, pound the sand (c) Scrape and tie the ventilation holes (d) Loosen the clamps, tap the core box (e) Open the core box, take out the sand core, and apply the coating
Basic operation of modeling
There are many methods of molding, but most of each method includes sand pounding, molding, repairing, and closing the box.
(1) molding
The original shape of the casting made of wood, metal or other materials is collectively referred to as the mold, which is used to form the cavity of the casting. Made of wood mold known as wood mold, made of metal or plastic mold known as metal mold or plastic mold. At present, most factories use wood mold. The shape of the mold is similar to the shape of the casting, the difference is that the casting, such as holes, in the mold is not only solid without holes, but also in the corresponding position to make the core head.
(2) Preparation before modeling
- ① Prepare molding tools, choose a flat base plate and a sand box of suitable size. If the sand box is too big, it will not only consume too much sand, but also waste sand pounding time. If the sand box is too small, the sand around the wooden mold will not be pounded tightly, and the liquid metal will easily flow out from the parting surface, i.e. between the interfaces, when pouring. Usually, the distance between the wooden mold and the inner wall and the top of the sand box should be 30-100mm, this distance is called the amount of sand. The specific value of sand consumption depends on the size of the wooden mold.
- ② Clean the wooden mold, so as not to molding sand sticking to the wooden mold, resulting in damage to the cavity when the mold.
- ③ When placing the wooden mold, pay attention to the direction of the slope on the wooden mold and don't put it in the wrong place..
(3)pound sand
- ① Pounding sand must be added to the sand in stages. For small sand box each time to add sand thickness of about 50 ~ 70mm. too much sand pounding is not tight, and too little sand and cost of labor. The first time to add sand must be used to press the sand around the wooden mold, so as not to move the position of the wooden mold in the sand box. Then use the pointed end of the hammer to pound the sand in several times, and finally use the flat end of the hammer to pound the top layer of sand.
- ② Pounding sand should be carried out in a certain route. Do not east a little, west a little chaotic pounding, so as to avoid the different parts of the tightness.
- ③ Pounding sand should be appropriate. Too much force, the sand is too tight, pouring the gas in the cavity can not run out. Too little force, the sand is too loose and easy to collapse the box. The tightness of each part of the same sand is different, close to the inner wall of the sand box should be pounded tightly to avoid the collapse of the box. Near the cavity part, the sand should be slightly tighter to withstand the pressure of liquid metal. Away from the cavity of the sand layer should be appropriately loose, in order to facilitate air permeability.
- ④ Pounding sand should be avoided to hit the wooden mold. General pounding hammer and wooden mold distance of 20 ~ 40mm, otherwise easy to damage the wooden mold.
(4) scattered fractional sand
Before building the sand model, a layer of fine-grained non-clay dry sand (i.e., modeling sand) should be sprinkled on the parting surface to prevent the upper and lower sandboxes from sticking together and not being able to open the box. Spreading sand, the hand should be slightly higher from the sand box, while turning around, while swinging, so that the parting sand through the finger cracks slowly and evenly scattered down, thinly covered in the parting surface. Finally, the wood mold should be blown off the parting sand, so as not to make on the sand mold, parting sand stick to the surface of the sand mold, and in the pouring of the liquid metal washed down into the casting, so that it produces defects.
(5)punch a hole in sth.
In addition to ensure that the sand has good air permeability, but also in the sand has been pounded and scraped flat, with a venting needle to tie out the ventilation holes, so that the gas is easy to escape when pouring. Ventilation holes should be vertical and evenly distributed.
(6)Open sprue
The outer gate should be dug into a 60° cone, with a diameter of about 60-80mm at the big end, and the surface of the gate should be polished, and the connection with the straight sprue should be made into a round transition to guide the liquid metal to flow smoothly into the sand mold. If the outer gate is dug too shallow and becomes disk-shaped, the liquid metal will splash around and hurt people when pouring.
(7)Doing the closing line
If the upper and lower sandboxes do not have locating pins, a closing line should be made on the wall of the sandbox before the upper and lower sand patterns are opened. The easiest way is to apply chalk dust on the wall of the box, and then use the scratching needle to draw a fine line. Need to go into the oven to bake the sand box, the sand clay is glued to the sand box wall, with a plasterer's knife sock flat, and then carve out the line, known as playing mud number. Close the box line should be located in the sand box wall at the furthest point of the two right-angled edges to ensure that the x and y directions can be positioned, and can limit the rotation of the sand type. The number of lines in two places should not be equal, so as not to make a mistake when closing the box. Do line finished, you can open the box mold.
(8)take up a mold
- ① Before taking up the mold, dip the water brush into some water and brush the sand around the wooden mold to prevent the sand cavity from being damaged when taking up the mold. Brush water should be a brush and not make the water brush stay in a place, so as to avoid excessive local water and produce a large amount of water vapor in the pouring, so that the castings produce porosity defects.
- ② mold needle position should try to coincide with the center of gravity of the wooden mold hammer line. Before starting the mold, use a small hammer to gently tap the lower part of the mold starting pin, so that the wooden mold is loosened, easy to start the mold.
- ③ When lifting the mold, slowly lift the wooden mold vertically, when the mold is about to be lifted all the way out, then take it out quickly. Be careful not to deflect and swing when lifting the mold.
(9) manicure
If the cavity is damaged after the mold is lifted, various repair tools should be used correctly according to the shape of the cavity and the degree of damage. If the damage of the cavity is large, the wooden mold can be put back into the cavity for repair, and then lifted out.
(10)close a case
Closing the box is the last process of molding, which plays an important role in the quality of the sand mold. Before closing the box, the sand mold should be carefully checked for damage and loose sand, and whether the sprue is repaired. If you want to put down the core, you should first check whether the core is dry, whether there is any damage and whether the ventilation holes are blocked. The position of the core in the sand mold should be accurate and stable, so as not to affect the accuracy of the casting, and to avoid being washed out by the liquid metal when pouring. When closing the box, attention should be paid to the upper sand box to keep the level down, and should be aligned with the closing line to prevent the wrong box. After closing the box, it is better to cover the sprue with paper or piece of wood to avoid sand or debris falling into the sprue.
Selection of casting pouring position and parting surface
castingsThe pouring position of the casting refers to the position of the casting within the mold during pouring.
The parting surface is the surface where the two halves of the casting come into contact with each other.
The main principle of their selection is to ensure the quality of castings and simplify the modeling process. In general, should first choose the pouring position after the decision of the parting surface, but in production due to the choice of the pouring position and the determination of the parting surface is sometimes contradictory to each other, we must comprehensively analyze the advantages and disadvantages of the various programs, choose the best program.
(1) .Principle of selection of casting position
- (A) the important processing surface of the casting should face down air holes, sand holes, slag, shrinkage holes are likely to appear in the upper surface, while the lower part of the metal liquid is relatively pure, the metal organization is relatively dense. Sometimes when the important machining surface is facing downward for reasons of difficulty, it should try to make it in the position of the example surface.
- (B) The large plane of the casting should be facing downward Due to the heat radiation effect during pouring, the sand on the upper surface of the casting cavity is easy to arch and crack, so that the upper surface of the casting produces sand and inclusion defects, so the large plane should be facing downward.
- (C) casting thin-walled part should be placed in the lower part of the thin-walled part is easy to produce pouring insufficient and cold segregation, so in the lower part of the mold can increase the filling pressure, improve the metal filling capacity.
- (D) should ensure that the casting to achieve directional solidification For alloy shrinkage, wall thickness of the casting is not uniform, the thickness of the large part of the casting should be placed in the casting of the uppermost or near the parting surface, in order to facilitate the placement of risers to achieve directional solidification
- (F) It should be easy to fix, install and exhaust the core and facilitate the closing of the mold.
(2).Principle of selection of parting surfaces
- (A) The parting surface should be selected at the largest cross-section of the mold to facilitate mold pickup, with particular attention paid to digging sand molding.
- (B) The number of parting surfaces should be minimized, and the use of three-box modeling should be avoided in mass production.
- (C) All or most of the castings shall be made in the same sand mold to reduce misboxing, flying edges and burrs and to improve the accuracy of the castings.
- (D) The number of cores and live blocks should be minimized can simplify the molding and core-making process and improve productivity.
Selection of process parameters
(1) Machining allowance
Castings need to be cut on the surface, should be set aside in advance a certain amount of machining allowance, its size depends on the type of casting alloy, modeling methods, casting size and processing surface in the casting of the location of many factors. Cast steel surface roughness, deformation, processing allowance; non-ferrous alloy surface is smooth, processing allowance is small; machine modeling high precision, processing allowance can be selected smaller; single piece of small batch production more factors affecting the processing allowance to increase; casting the larger, more complex, the larger the processing allowance; casting casting of the top surface than the bottom and the side of the machining allowance is large.
Single piece of small batch production of small cast iron pieces of machining allowance of 4.5 ~ 5.5mm; small non-ferrous metal castings machining allowance of 3mm; gray cast iron pieces of machining allowance value can refer to JB2854-80.
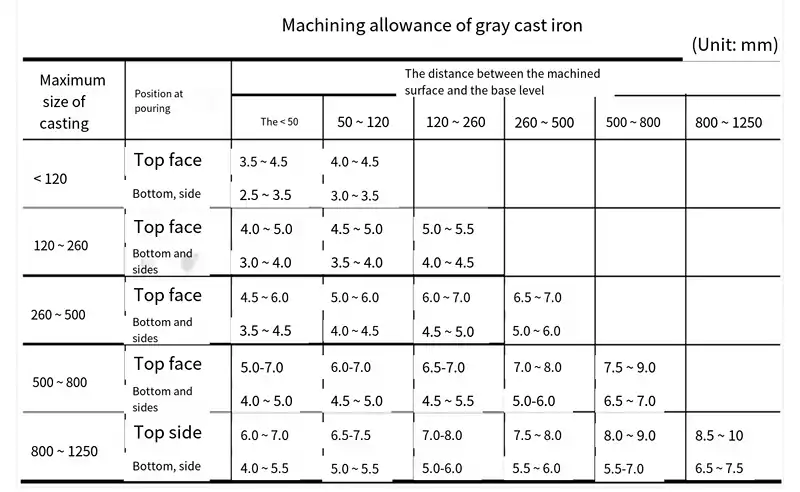
In addition, cast steel parts on the diameter of less than ф35mm and cast iron parts on the diameter of less than ф25mm holes are generally not cast, left to machining more economical and convenient. For machine modeling of small parts, not cast out of the hole can be smaller. For special shapes that do not require processing, machining difficulties in the hole, slot, it must be cast.
(2) Molding Slope
In order to make the prototype easy to take out from the casting, perpendicular to the parting surface of the vertical wall added to the slope of the mold for the starting slope. The higher the mold, the smaller the value of the slope, and the slope of the inner wall is larger than that of the outer wall. The inner wall slope is bigger than the outer wall slope. The slope of hand molding is bigger than that of machine molding. When the mold is short (≤100mm), it is about 3º, and when the mold is high (101~160mm), it is 0.5°~1°.
(3) Casting rounded corners
In order to prevent the casting in the wall of the connection and corners of the stress and cracks, to prevent the casting of the sharp corners of the damage and the generation of sand eyes, in the design of the casting casting wall of the connection and corners of the part should be designed into four corners.
(4) Core Heads
In order to ensure the positioning, fixing and venting of the core in the casting mold, both the mold and the core are designed with a core head.
The core head is the outstretched part of the core, which falls into the core seat of the casting model and plays the role of positioning and supporting the core.
The shape of the core head depends on the type of core, the core head must have enough height (h) or length (l) and suitable slope, in order to make the core convenient, accurate and firmly fixed in the casting mold, so as to avoid the core in the pouring floating, deflection and movement
(5) Shrinkage allowance
As the casting in the cooling contraction after pouring, the production of mold to add this part of the shrinkage of the size. General gray cast iron shrinkage allowance of 0.8% - 1.0%, cast steel for l.8% - 2.2%, cast aluminum alloy for 1.0% - 1.5%. The size of the shrinkage allowance in addition to the type of alloy, but also with the casting process, castings in the contraction of the blocking situation and so on.
| Alloy Type | Casting Shrinkage | ||
| free contraction | shrinkage | ||
| gray cast or found metals unshakeable | Small and medium-sized castings | 1.0 | 0.9 |
| Medium and large castings | 0.9 | 0.8 | |
| Extra large castings | 0.8 | 0.7 | |
| ductile iron | 1.0 | 0.8 | |
| Carbon and low alloy steel | 1.6~2.0 | 1.3~1.7 | |
| tin bronze | 1.4 | 1.2 | |
| Wuxi Bronze | 2.0~2.2 | 1.6~1.8 | |
| silicon brass | 1.7~1.8 | 1.6~1.7 | |
| aluminum-silicon alloy | 1.0~1.2 | 0.8~1.0 | |
Advantages and disadvantages of sand casting
Advantages of sand casting
- Low manufacturing costs: Sand casting uses raw materials (e.g., sand, clay, etc.) at low cost, and the manufacturing process is relatively simple, so the manufacturing cost is relatively low.
- High manufacturing flexibility: Sand casting can produce castings of various shapes and sizes, from a few grams to several tons of parts with ease and great applicability.
- Short manufacturing cycle: The sand casting process is relatively simple and requires less drying and hardening time, resulting in a relatively short manufacturing cycle.
- Wide range of raw material sources: Sand casting has a wide range of raw material sources, sand, clay, etc. can be used as modeling materials, and cheap.
Disadvantages of sand casting
- Average surface quality of castings: The surface quality of sand casting castings may have some defects, such as sand holes, sand holes, sticky sand and so on.
- The sand core is prone to collapse: In sand casting, sand cores may be required to manufacture castings with complex shapes. Sand cores are prone to deformation and collapse, resulting in a high rate of rejects.
- Lower productivity: Sand casting is relatively unproductive because each sand mold needs to be made by hand and the casts can only be used once.
- High energy consumption and high pollution emissions: Sand casting consumes high energy during the production process and may produce certain polluting emissions, such as dust and exhaust gases. This may have some impact on the environment and workers' health.

























