Semi-solid metal casting process
Date: 2024-08-03 Categories: Blog Views: 5167
1. Overview
Since 1971, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's D.B. Spencer and M.C. Flemings invented a stir casting (stir cast) new process, that is, using a rotating double barrel mechanical stirring method to prepare a Sr15% Pb rheological slurry since the semi-solid metal (SSM) casting process technology has experienced more than 20 years of research and development. The alloys prepared by stir casting are generally known as non-dendritic organization alloys or called Partially Solidified Casting Alloys (Partially Solidified Casting Alloys). Products using this technology have a strong vitality due to their high quality, high performance and high alloying characteristics. In addition to applications in military equipment, it began to focus mainly on key components for automobiles, for example, for automobile wheels, which can improve performance, reduce weight, and lower the scrap rate. Since then, it has gradually gained applications in other fields to produce high-performance and near-net-forming components. Semi-solid metal casting process forming machinery has also been introduced. Has been developed and produced from 600 tons to 2000 tons of semi-solid casting die-casting machine, forming parts weight up to 7kg or more. At present, in the United States and Europe, the process technology is more widely used. Semi-solid metal casting process is considered to be the 21st century the most promising near-net forming and one of the new material preparation technology.
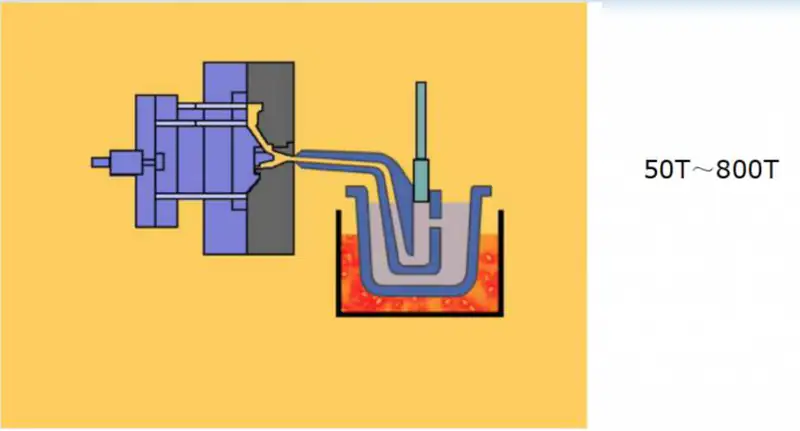
2、Process Principle
The principle of the semi-solid casting process lies in the fact that by applying strong agitation during the solidification of the liquid metal, the dendritic network skeleton formed in conventional casting is broken and transformed into a dispersed granular organization suspended in the liquid phase. This semi-solid slurry in the solid phase rate reaches a certain level (such as 0.5-0.6) can still maintain a certain degree of fluidity, making it possible to use theDie castingConventional forming processes such as extrusion, die forging, etc. process the metal to optimize the quality of the casting and increase productivity.
3、Alloy preparation
There are many methods to prepare semi-solid alloys, in addition to the mechanical stirring method, in recent years, electromagnetic stirring method has been developed, electromagnetic pulse loading method, ultrasonic vibration stirring method, forced flow of the alloy liquid along the curved channel under the action of external force, strain-induced melting activation method (SIMA), spray deposition method (Spray), control of alloy casting temperature method, and so on. Among them, the electromagnetic stirring method, the method of controlling the alloy casting temperature and the SIMA method are the methods with the most potential for industrial application.
3.1 Mechanical mixing method
Mechanical stirring was the earliest method used for the preparation of semi-solid alloys.Flemings et al. successfully prepared semi-solid slurries of tin-lead alloys by using a stirring set consisting of a concentric inner and outer cylinders with teeth (the outer cylinder rotating while the inner cylinder was stationary); H. Lehuy et al. used stirring paddles for the preparation of Aluminum-Copper alloys, Zinc-aluminumand aluminum-silicon alloy semi-solid slurry. The later improved the stirrer and prepared the ZA-22 alloy semi-solid slurry by using a spiral stirrer. Through the improvement, the stirring effect of the slurry was improved, the overall flow strength of the metal liquid in the mold was strengthened, and the downward pressure of the metal liquid was generated to promote pouring and improve the mechanical properties of the ingot.
3.2 Electromagnetic stirring method
Electromagnetic stirring is the use of rotating electromagnetic field in the metal liquid to produce induced current, the metal liquid in the Lorentz magnetic force under the action of the movement, so as to achieve the purpose of stirring the metal liquid. At present, there are two main methods to generate rotating magnetic field: one is the traditional method of passing alternating current inside the induction coil; the other is the rotating permanent magnet method introduced by C.Vives of France in 1993, the advantage of which is that the electromagnetic inductor is composed of high-performance permanent magnetic material, the magnetic field generated inside is of high strength, and by changing the arrangement of permanent magnets, it can make the metal liquid produce an obvious three-dimensional flow and improve the The stirring effect is improved and the gas involvement during stirring is reduced.
3.3 Strain Induced Melt Activation Method (SIMA)
Strain Induced Melting Activation (SIMA) is a process whereby a conventional ingot is pre-deformed, e.g. hot worked by extrusion, rolling, etc., into a semi-finished bar, which has a microstructure with a strong elongated deformation structure, and then heated to the solid-liquid two-phase region isothermal for a certain period of time, where elongated grains are turned into fine particles, and then cooled rapidly to obtain an amorphous ingot with an amorphous organization.The effectiveness of the SIMA process depends mainly on the lower temperature and remelting stages, or on the addition of a cold working stage in between. The effect of SIMA process mainly depends on the lower temperature of the hot working and remelting two stages, or between the two add a cold working stage, the process is more controllable.SIMA technology is suitable for a variety of high and low melting point alloy series, especially for the preparation of higher melting point of non-dendritic alloy has a unique superiority. Has been successfully applied to stainless steel, tool steel and copper alloys, aluminum alloy series, to obtain the grain size of about 20um non-dendritic organization of the alloy, is becoming a competitive method of preparing semi-solid forming raw materials. However, its biggest drawback is the small size of the prepared blanks.
3.4 New methods developed in recent years
In recent years, Southeast University and the Aresty Institute in Japan have found that the incipient dendritic organization can be transformed into a spheroidal organization by controlling the casting temperature of the alloy. The method is characterized by the fact that there is no need to add alloying elements nor stirring.V.Dobatkin et al. proposed a method of obtaining semi-solid ingots by adding a refining agent to the liquid metal and ultrasonically treating them, which is called the ultrasonic treatment method.
4. Molding method
There are many methods of forming semi-solid alloys, the main ones being:
(1) Rheocasting(Rheoforming, Rheocast) The direct die casting or extrusion molding of the resulting semi-solid metal slurry by intense agitation during the cooling of the metal liquid from the liquid phase to the solid phase at a certain solid phase fraction. 1 Die casting alloy 2 Continuous supply of alloy liquid 3 Induction heater 4 Cooler 5 Rheologically cast ingot 6 Injection chamber 7 Die casting mold For example, R. Shibata et al. have shaped a semi-solid alloy slurry prepared by the electromagnetic stirring method by feeding it directly into the injection chamber of a die casting machine. The mechanical properties of aluminum alloy castings produced by this method are higher than those of extrusion castings and comparable to those of semi-solid thixotropic castings. The problem is, semi-solid metal slurry preservation and transportation is difficult, so the actual put into application is not much.
(2) Thixotropic casting(Thixoforming, Thixocast) Die casting or extrusion of prepared ingot billets with non-dendritic organization after reheating them to the solid-liquid two-phase region to achieve the appropriate viscosity. EOPCO, HPM Corp., Prince Machine, and THT Presses of the United States, as well as Buhler of Switzerland, IDRA USA and Italpresse of America of Italy, Producer USA of Canada, Toshiba Machine Corp. and UBE Machinery Services of Japan have been able to produce semi-die casting. Machinery Services, etc. have been able to produce semi-solid aluminum alloys into the shape of the special equipment. The method of billet heating, transportation is easy to realize the automation, so it is today's semi-solid casting of the main process methods.
(3) Injection molding(Injection Molding) directly to the molten metal liquid (rather than after treatment of semi-solid slurry) cooled to the appropriate temperature, and supplemented by a certain process conditions into the cavity molding. Such as the United States of America Wisconsin touch into the shape of the development center, had used the method of semi-solid casting of magnesium alloys. Cornell University of the United States, Professor K.K. Wang and others developed a similar magnesium alloy shot casting forming device, the semi-solid slurry from the tube to join, after appropriate cooling pressure injection into the cavity.
(4) Low temperature continuous casting The so-called low-temperature continuous casting is a casting method in which the superheat of the liquid metal is controlled to be around 0°C and forced cooling is carried out underneath the casting mold. Center segregation is a big problem in continuous casting, and breakage may occur in continuous rolling of wire rod. Therefore, the process is of great significance.
(5) Strip continuous casting Flemings has carried out experimental studies on strip continuous casting with Sn-15% Pb low melting point metal, analyzing heat transfer, solidification and deformation. It was concluded that the strip thickness was related to roll pressure, solid phase rate, rheological shear rate and continuous casting speed. When the specific pressure under extrusion is high, it promotes microsegregation. In order to ensure the surface and internal quality and dimensional accuracy, it is necessary to strictly control the process parameters of semi-solid metal manufacturing, such as the solid phase rate, the size of the initial crystalline form and the amount of emitted metal. For high melting point metals such as phosphor bronze Cu-Sn-P alloy (Cu-8%Sn-0.1%P), the liquid phase line temperature of 1030 ℃, difficult to hot work, with this semi-solid alloy made of thin plate has obvious results. At present, it has been possible to prepare excellent organization of semi-solid stainless steel ingots, high-speed tool steel ingots.
5 Technological advantages
The advantages of semi-solid die casting technology include both product and process advantages.
(1) Process Advantages
(1) do not need to add any grain refining agent to obtain fine grain organization, eliminating the traditional casting of columnar crystals and coarse dendritic crystals.
(2) Low forming temperature (such as aluminum alloy can be reduced by more than 120 ℃), can save energy.
3) Extended mold life. Because of the lower temperature of the semi-solid slurry molding shear stress, than the traditional dendritic slurry is three orders of magnitude smaller, so the filling smooth, small thermal load, thermal fatigue strength decreased.
4) Reduce pollution and unsafe factors. Because the operation is free from high temperature liquid metal environment.
(5) Small deformation resistance, the use of small force can be achieved homogeneous processing, easy to form difficult-to-machine materials.
(6) Faster solidification, higher productivity and shorter process cycle.
(7) Suitable for the use of computer-aided design and manufacturing, improving the degree of automation of production.
(2) Product Advantage
1)Quality of castingsHigh. Due to grain refinement, uniform tissue distribution, body shrinkage reduction, thermal cracking tendency to decline, the matrix to eliminate the tendency to shrink loose, mechanical properties greatly improved.
(2) Solidification shrinkage is small, so after molding high dimensional accuracy, small machining allowance, near net molding.
(3) Wide range of forming alloys. Non-ferrous alloys are aluminum, magnesium, zinc, tin, copper, nickel-based alloys; iron-based alloys are stainless steel, low alloy steel, etc..
(4) Manufacture of metal matrix composites. Utilizing the high viscosity of semi-solid metals, it is possible to make alloys of metals with large density differences and small solid solubility, and it is also possible to effectively use a mixture of different materials to make new composite materials.
6, the development of semi-solid casting technology
6.1 Influence of temperature interval perturbation and pouring temperature on the as-cast organization of magnesium alloys in the semi-solid state
AZ91HP magnesium alloy in stainless steel crucible resistance furnace heating to 720 ℃ insulation 10 minutes for refining treatment, in the liquid phase line near the short-term insulation treatment, can reduce the tendency of dendritic organization formation; reduce the processing temperature, the melt is disturbed to accelerate the development of grains to the equiaxial or even spherical; in the semi-solid temperature range of the melt blowing argon (Ar) treatment, so that the melt is disturbed to improve the nucleation rate. Accelerated the fusion of dendritic arms and grain equiaxialization, can get a uniform distribution of non-dendritic organization; this makes the forming of semi-solid castings, the hard and brittle β-phase content is reduced, and is a fine mesh distribution in the incipient α-phase grain boundaries, improve the mechanical properties of magnesium alloy semi-solid castings (Foundry, 2006, 55 (2): 120-125).
6.2 Advanced pulping methods for semi-solid alloys
Among the advanced slurry making methods that have been proposed, the tilted plate technology is simple in principle and equipment, easy to control the process, and low cost. Using the tilted plate method to prepare semi-solid sub-eutectic high chromium white cast iron semi-solid slurry device, the metal liquid in the cooling body under the action of excitation cooling, austenite in a non-uniform manner a large number of nucleation and growth, dendritic melting, folding, crushing and thus refinement, the formation of spherical austenite.
6.3 Semi-solid thixotropic die casting of Al-6Si-2Mg aluminum alloy
Al-6Si-2Mg aluminum alloy with liquid phase line temperature of 615°C and solid phase line temperature of 557°C has excellent thixotropic process performance. Bar billet using hot top method, electromagnetic stirring vertical semi-continuous casting, diameter of 60 ~ 70mm; billet in the medium frequency induction equipment coil heating, the beginning of rapid heating to 500 ℃, and then slow heating, the core up to 560 ℃, and further reduce the heating power, in the core to 575 ℃, moved to 2800KN horizontal cold chamber die casting machine, die casting into the automobile engine on the use of water pump cover. Semi-solid die casting, has melted α-Al in die casting high-speed shear contact into shape, part of the primary α-Al grows up, part of the solidification into a fine spherical secondary α-Al. Eutectic organization in the Mg2Si than continuous casting organization is more fine; Because of semi-solid organization in the absence of air holes, by 540 ℃, 8 hours of solid solution treatment after quenching, and then by 170 ℃, 6 hours of artificial aging, obtain the following Mechanical properties: tensile strength 340MPa, yield strength 310MPa, elongation 3.5% (Casting, 2005, 54(5): 475-478).

























