Differential pressure casting process and principle
Date: 2024-11-27 Categories: Blog Views: 4195
What is differential pressure casting?
differential pressure casting(also known as counterpressure casting), is a liquid metal in the differential pressure, filled to a certain pressure in advance of the casting, crystallization, solidification and obtain a casting of a process method. It isLow-pressure castingCombination of two processes: crystallization and solidification under pressure.
The process can be based on the shape of the casting, process requirements and casting characteristics, adjust the pressure in the cavity, so that the liquid metal is controlled to flow into the casting, and does not change the casting force state conditions, so that the casting is solidified at a higher pressure, to produce a complex, thin-walled, whole aluminum casting difficult to pour with other molding methods, to solve the casting casting technology, a major ke.
Differential Pressure Casting Principle of Operation.
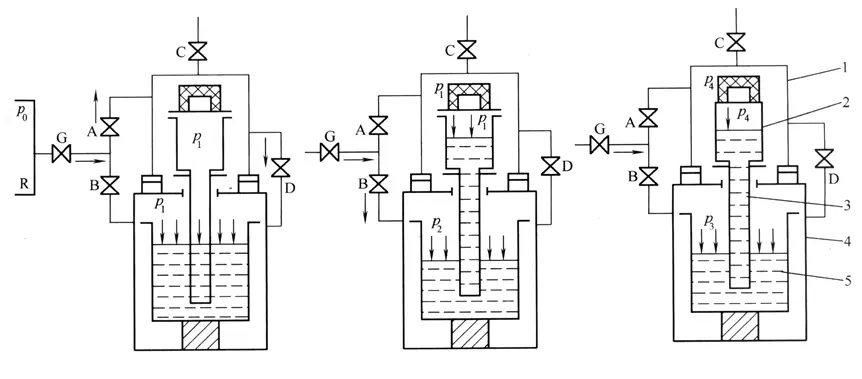
A. Inflatable
B. Pressurization
C. Stress Reduction
The mold is placed in the upper pressure cylinder, the crucible furnace is placed in the lower pressure cylinder, the upper and lower pressure cylinders are separated by a diaphragm, and the liquid-raising tube connects the mold with the holding furnace.
Metal liquid filling methods are:
1) Pressurization method:
2) Stress reduction method:
Differential pressure casting process characteristics:
Because the differential pressure casting metal liquid is under a certain pressure filling, so bring a series of factors conducive to obtaining high quality castings.
(1) Charging speed can be controlled; different differential pressure ⊿P-charging speed can be obtained to obtain the optimal charging speed;
(2) The best quality mold filling liquid can be obtained, and foreign inclusions can be prevented from entering the mold.
(3) Due to crystallization and solidification under high pressure, the casting conditions are improved, thus greatly improving the density of the casting; the casting can be up to 0.25 mm thick locally and has a clear contour.
(4) in the pressure preservation period, the casting is still in a high-pressure state, under the action of external pressure, will produce a small amount of plastic deformation, thereby reducing the "micro-shrinkage", improve the mechanical properties of the casting; compared with the low-pressure casting, differential pressure casting casting tensile strength can be increased by 10-50%, elongation can be increased by 25-50%.
(5) crystallization and solidification under high pressure, and can improve the solubility of the gas in the metal liquid, which can greatly reduce the casting of the "gas hole" and "pinhole" defects.
(6) Improvement of casting surface quality ---- Due to the adjustability of differential pressure ⊿P, it is possible to reduce "cold segregation" and "mechanical sand sticking" by differential pressure ⊿P;
(7) Controlled atmosphere pouring can be realized;
(8) Facilitates mechanization and automation, increases labour productivity, reduces clean-up workload and improves labour conditions.
Comparison of Mechanical Properties of Differential Pressure Casting and Low Pressure Casting Aluminum Alloys
| Casting method | mechanical property | ZL101 | ZL102 | ||
| Wall thickness 5mm | Wall thickness 20mm | Wall thickness 5mm | Wall thickness 20mm | ||
| differential pressure casting | Tensile strength σb/Mpa | 171 | 190 | 190 | 184 |
| Elongation at break δ/% | 8.0 | 7.2 | 6.5 | 6.5 | |
| Low-pressure casting | Tensile strength σb /Mpa | 171 | 132 | 168 | 143 |
| Elongation at break δ/% | 4.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 2.0 | |
Structural design of differential pressure casting equipment
Differential pressure casting equipment has three main components: mainframe, pressure control, air supply
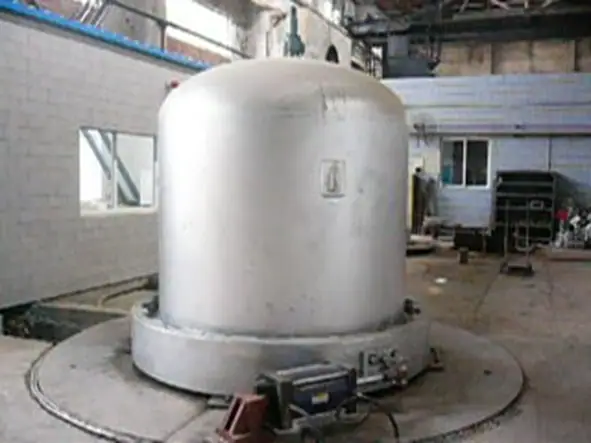

Differential pressure casting equipment profile
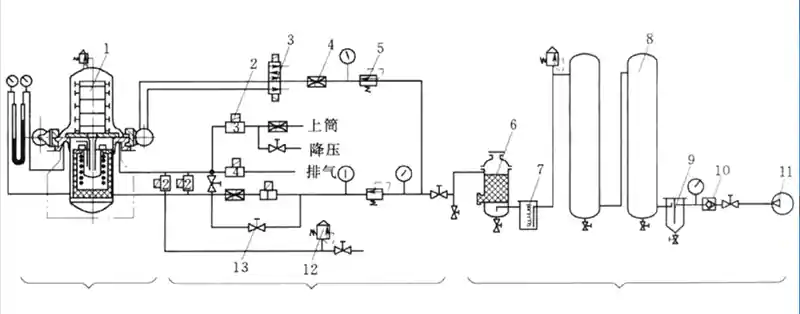
Main equipment section
Pressure control section
air supply component
1) Pressure tank design: Head section
2) Locking mechanism
3) Inflating method: air control system and its attached devices
Differential pressure casting casting process design
1) Selection of casting position
Establish the pouring location, to make the casting from away from the sprue first solidification, sprue last solidification, realize the casting sequence solidification, often the casting thin-walled parts away from the sprue, so that the liquid metal from the thick-walled place to introduce, and the low-pressure casting casting location is the same as the selection of the choice of the location of the pouring.
2) Machining allowance and process allowance
For castings with uniform wall thickness, in order to realize sequential solidification in the direction of the gate, it can be taken to increase the machining allowance, and the non-machined plane can be used as a process allowance, so that the wall thickness of the casting increases in the direction of the sprue.
3) Selection of casting system
(1) Requirements to be met by a reasonable casting system
① On the premise of ensuring the smooth charging of the metal liquid, the charging should be fast.
② Favorable for slag blocking and exhaust.
③ It is favorable for the casting to realize sequential solidification.
(2) Form of casting system
Generally choose the bottom injection type pouring system, aluminum, magnesium alloy castings often use open type pouring system, for the height of castings greater than 300mm, can choose the slit type pouring system.
4) Risers and Cold Iron
Differential pressure casting effectively strengthens the riser's complementary shrinkage effect, therefore, for individual thick hot joint parts, generally only need to use the dark riser. Cold iron is often used in conjunction with the risers and sprue to accelerate the cooling rate of the casting at the local hot joints, so that the hot joints and the adjacent connecting wall solidification at the same time, in order to achieve the purpose of the entire casting sequential solidification.
Differential pressure casting pouring process
(1) Characteristics of the pouring process of differential pressure casting
Differential casting pressurization is divided into 6 stages
0 to t1: inflation phase
t1 to t2: Pressure equilibrium phase
t2~t3: Liquid Lifting Stage
t3~t4: Charging phase
t4~t5: Pressure holding phase
t5 to t6: Interconnection phase
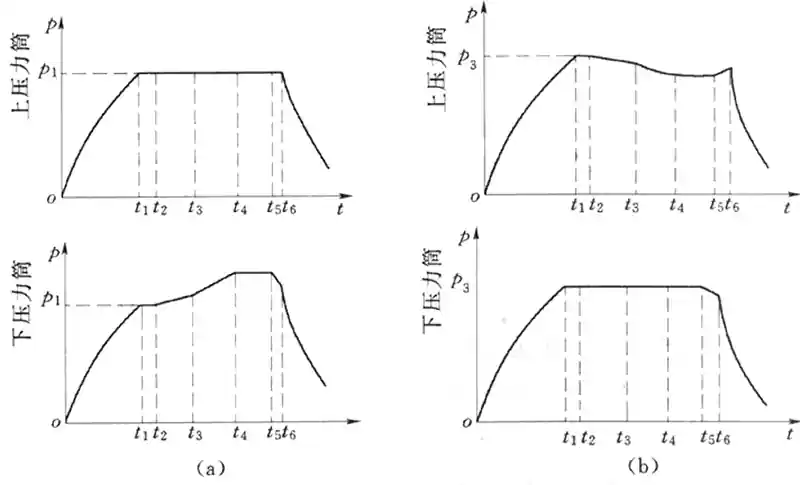
pressurization
decompression schedule
Comparison of stress-boosting and stress-reducing methods
Pressurization method: From the characteristic curve, it can be seen that the line segment of the pressurization curve a'b' is poor, and the filling speed of the liquid metal will fluctuate.
Decompression method: The ab section accounts for a small proportion of the entire curve and is very close to a straight line, therefore, the decompression method has a smooth rise of the metal liquid.
Selection of process parameters
(1) Charge pressure difference Δp
can be calculated as p=HρK/10200
(2) Crystallization pressure
The higher the crystallization pressure, the denser the casting, the better the mechanical properties of the casting. Crystallization pressure and casting structure, alloy crystallization characteristics and other factors.
(3) Lifting speed
In order to keep the metal liquid smoothly and slowly rising liquid. To avoid spattering, the liquid should be lifted slowly.
(4) Charging speed
The filling speed should be faster than the rate of liquid rise, but should not be too fast, to prevent the generation of secondary inclusions. Filling speed and casting complexity, wall thickness, size and alloy type related to the type of casting used.
(5) Holding time
The holding time should be approximately the same as the solidification time of the casting. Holding time and casting size, wall thickness, alloy type and crystallization pressure and so on. The thicker the casting wall thickness, the wider the alloy crystallization temperature range, the longer the holding time.
(6) Pouring temperature
Differential pressure casting pouring temperature is higher than the generalGravitational castingCould be lower.aluminumThe pouring temperature can be as low as 306~0℃.
Differential Pressure Casting Applications
Differential die casting is suitable in addition to the available sand type, can also be used for metal type. Single piece, small batch production can be used in sand, production of large quantities, can be used in metal type. The weight of castings can be from less than 1kg to more than 100kg.
At present, China's largest casting diameter of 540mm, height of 890mm, wall thickness of 8 ~ 10mm large complex thin-walled whole cabin castings. The alloys that can be cast are aluminum alloy, zinc alloy, magnesium alloy, copper alloy, and cast steel. The castings produced include motor shells, valves, impellers, cylinders, wheel hubs, tank guide wheels, ship hulls, and so on.
In the pressure casting machine production by the projected area or wall thickness limitations of the casting can be used to produce differential pressure casting method.

























