In-depth analysis of the entire friction welding process
Date: 2025-03-08 Categories: Blog Views: 544
Friction welding definition
Friction welding is the use of relative friction movement of the weldment to realize the heat generated by the relative friction of the material to achieve a reliable connection of a pressure welding method. The welding process is under the action of pressure, the relative movement of the material to be welded between the friction, so that the interface and its nearby temperature rises and reaches a thermoplastic state, with the role of the top forging force of the interface oxide film is broken, the material undergoes plastic deformation and flow, through the interface of the elements of the diffusion and recrystallization of metallurgical reaction and the formation of joints.
Friction welding principle
Two metal workpieces of circular section are clamped in a chuck which can be rotated and a chuck which can be moved forward and pressurized, respectively, before friction welding. At the beginning of welding, the workpiece 1 rotates at high speed, the workpiece 2 moves and contacts in the direction of the workpiece 1, and a sufficiently large friction pressure is applied to start the friction heating process. After friction for a period of time, the temperature of the joint metal reaches the welding temperature, stop the rotation of the workpiece 1, and at the same time, the workpiece 2 moves rapidly to apply the top forging pressure, so that it produces the top forging deformation, and completes the welding.
Friction welding classification
There are many methods of friction welding, generally categorized according to the relative motion of the weldment and the characteristics of the process, the main methods include:
- Continuous drive friction welding
- Phase controlled friction welding
- inertial friction welding
- friction stir welding
- Embedded friction welding
- friction welding of the third body
- Friction cladding
Continuous friction welding
Under the action of friction pressure, the welded interfaces are in contact with each other, and through relative motion friction, mechanical energy is converted into thermal energy, and the friction heat is utilized to remove the oxides at the interfaces, and a reliable joint is formed under the action of the top forging force. This is a common type of friction welding, in the welding process, the workpiece is continuously driven by the spindle motor, rotating at a constant speed, until it reaches the specified friction time or friction deformation, the workpiece immediately stops rotating and top forging welding.
inertial friction welding
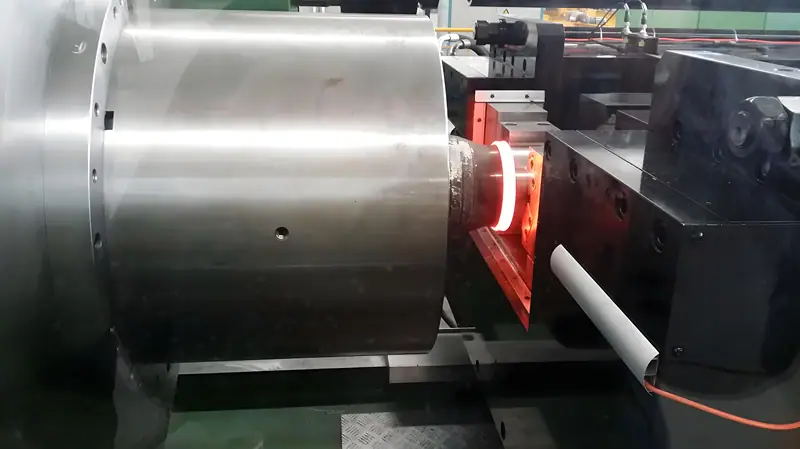
The rotating end of the workpiece is clamped in the flywheel, and the welding process starts by accelerating the flywheel and the rotating end of the workpiece to a certain rotational speed, and then the flywheel is disengaged from the main motor, and the moving end of the workpiece moves forward to start friction heating. The flywheel is braked by the friction torque, the speed is gradually reduced and the welding process ends when the speed is zero.
phase friction welding
Mainly used for relative position requirements of the workpiece, such as hexagonal steel, octagonal steel, automotive joystick, etc., requires that the prongs are aligned after welding, the direction of the right or phase to meet the requirements. The main methods are:
- Mechanical synchronized phase friction welding
- Pin Fitting Friction Welding
- Synchronized Drive Friction Welding
Radial friction welding
The pipe to be welded is beveled, with a mandrel inside the pipe, fitted with a rotating ring with a beveled surface, which rotates and applies radial friction pressure to the two pipes during welding, and the top forging pressure is applied at the end of friction heating.
Friction cladding
The cladding metal round bar rotates at high speed and exerts frictional pressure on the base metal. Due to the large volume of the base metal, the heat conduction is good and the cooling speed is fast. So that the friction surface from the cladding metal and base metal interface to the cladding metal side. At the same time, the cladding metal condenses and transitions to the base metal to form cladding weld flesh. When the base metal rotates or moves relative to the cladding metal bar, a surfacing weld is formed on the base metal.
linear friction welding
To be welded two workpieces a fixed, another at a certain speed for reciprocating motion, or two workpieces for the relative reciprocating motion, under the action of the pressure of the two workpieces of the interface friction generates heat, so as to realize the welding.
friction stir welding
Will be a high-temperature resistant hard material made of a certain shape of the stirring needle rotating deep into the two welded materials connected to the edge of the stirring head to adjust the rotation of the two weldments connected to the edge of a large amount of frictional heat, which in the connection of the plastic softening of the metal produced in the connection of the area, the plastic softening of the area in the stirring head under the action of the stirring, extrusion, and with the stirring head of the rotating along the weld backward flow, the formation of a plastic metal flow, and stirring the head away from the cooling process and extrusion and formation of solid phase welded joints. The plastic soft zone is stirred and squeezed under the action of the stirring head, and flows backward along the weld seam with the rotation of the stirring head, forming a plastic metal flow, and in the cooling process after the departure of the stirring head, it is squeezed and forms a solid phase welded joint.
Orbital friction welding
Orbital friction welding is a newly developed welding method, mainly used for welding non-circular section workpiece. Linear orbital friction welding workpiece along the straight rail, with a certain amplitude and frequency to ensure that the vibration speed to reach the required value, so that the welding surface to do relative repeated vibration friction. Circular orbit friction welding workpiece of each mass to the same radius and speed, along the circular orbit to make the welding surface to do the relative movement of friction. When the joint is heated to the welding temperature, the friction movement of the workpiece is stopped and the top welding is carried out.
Friction Welding Welding Process
Process Characteristics
vantage:
- Short welding construction time and high productivity.
- Low welding distortion and high dimensional accuracy after welding.
- High degree of mechanization and automation, stable welding quality.
- It is suitable for welding all kinds of dissimilar materials, and can weld aluminum-steel, aluminum-copper, titanium-copper, intermetallic compounds-steel, etc., which cannot be welded under conventional melting.
- Welding of rods and tubes of the same and different diameters is possible.
- Welding does not produce smoke, arc light and harmful gases and does not pollute the environment.
Disadvantages.
1. It is more difficult to weld non-circular cross-section, and the required equipment is complicated; it is also more difficult to weld disc-shaped thin parts and thin-walled pipe fittings because they are not easy to clamp.
2. It is difficult to realize friction welding for components whose shapes and assembly positions have already been determined.
3. The joints are prone to fretting and must be machined after welding.
4. The clamping area is prone to scratches or clamping marks
Friction welding process
Friction welding is a highly efficient solid-state joining technique that centers on the metallurgical bonding of materials using frictional heat and mechanical forces. The process begins with the precise fixing of the workpiece - usually one side of the workpiece is held firmly in place by a fixture, while the other side is connected to a rotary drive that ensures that the two contact surfaces are clean and flat. When the machine is started, the rotating workpiece comes into close contact with the stationary part under axial pressure, and the high-speed friction instantly generates high temperatures at the interface, which quickly penetrate into the material and bring it to a plastic state. In this process, the friction not only breaks the oxide layer on the surface, but also promotes the dynamic recrystallization of the metal lattice, forming a flowing softened layer. When the temperature accumulates to the critical point, the equipment decisively stop rotating, and then apply greater pressure of the top forging, at this time, the softened material as if it were forged like the extrusion and fusion, the microscopic level of the atomic diffusion and grain boundary migration completely eliminate the defects of the joint surface, forming a dense and flawless welded joints. After cooling and shaping, the weldment is virtually deformation-free and its strength can even exceed that of the base material.
Common Friction Welding Equipment
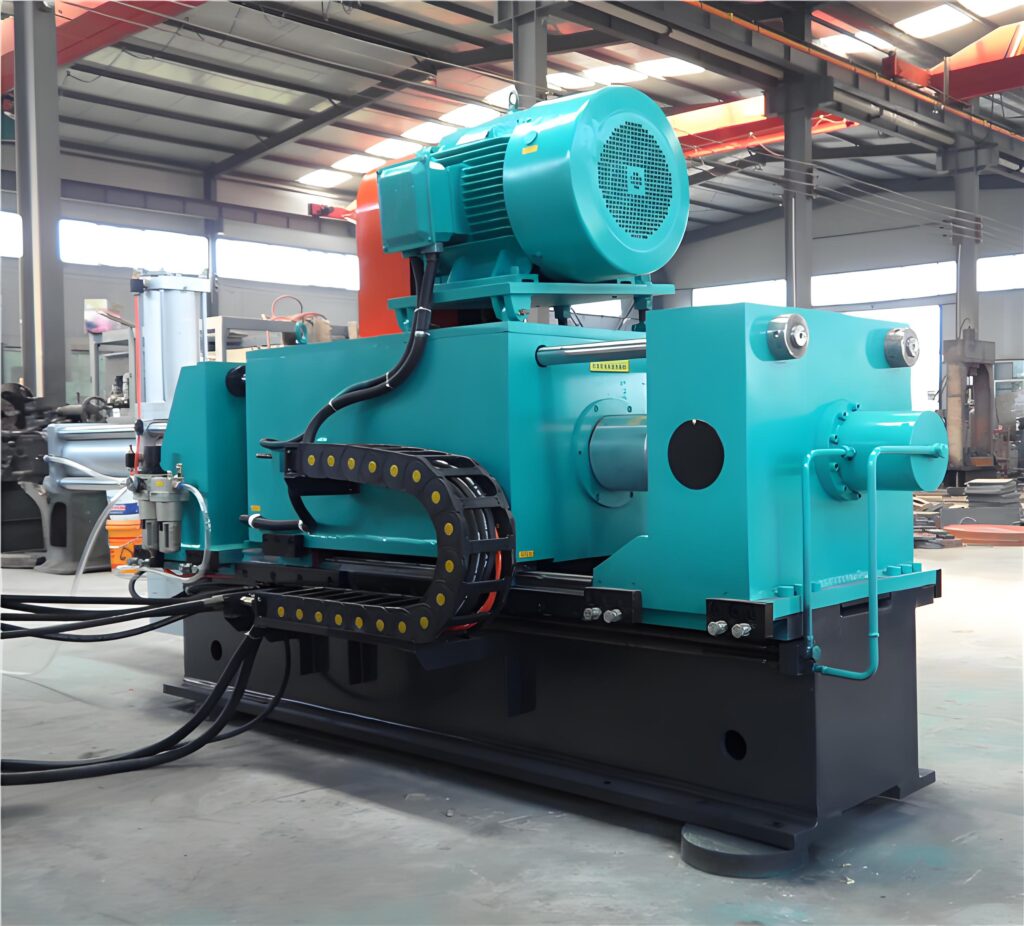

Conventional friction welding equipment
The traditional friction welding equipment is solidly connected to the high-precision pressure control mechanism through the mechanical drive system, the core of which consists of the spindle power module, hydraulic pressurization device and intelligent control system. The equipment adopts modular design, which can be flexibly adapted to the clamping requirements of shafts, tubes and shaped workpieces, realizing efficient welding of key engine components in the automotive manufacturing field, and relying on the real-time monitoring system to complete the reliable connection of high-strength alloy materials in the military field. Compared with the traditional welding process, the equipment has significant advantages in energy consumption control and joint quality, with multi-sensor fusion technology, can meet the aerospace, rail transportation and other industries on the stringent requirements of precision welding, and become the core equipment for high-volume industrialized production.
Friction Stir Welding Equipment
Friction Stir Welding (FSW) equipment is an advanced welding equipment developed based on the principle of solid-state joining, and its core innovation lies in the use of special stirring head to realize the plastic flow and metallurgical combination of materials. The equipment mainly consists of high rigidity body, rotary drive system, precision temperature control module and three-dimensional force position sensing unit. Through the synergistic action of stirring needle and shaft shoulder, it can complete the welding process without melting.aluminumThis technology has been widely used in the aerospace industry to realize the integrated molding of skin-skeleton and the manufacturing of battery tray for new energy vehicles. Compared with traditional friction welding, this technology significantly improves the welding quality of thin plate, realizes integrated molding of skin-skeleton in the aerospace field, and is widely used in the manufacture of battery trays for new energy vehicles, and the strength of weld seam can reach more than 95% of the base material. The latest equipment integrates visual guidance and adaptive control algorithms, which can dynamically adjust welding parameters and successfully break through the bottleneck of joining technology for dissimilar materials (e.g. aluminum/copper, aluminum/steel).


















