Aluminum die casting mold design and manufacturing
Date: 2024-08-05 Categories: Blog Views: 1800
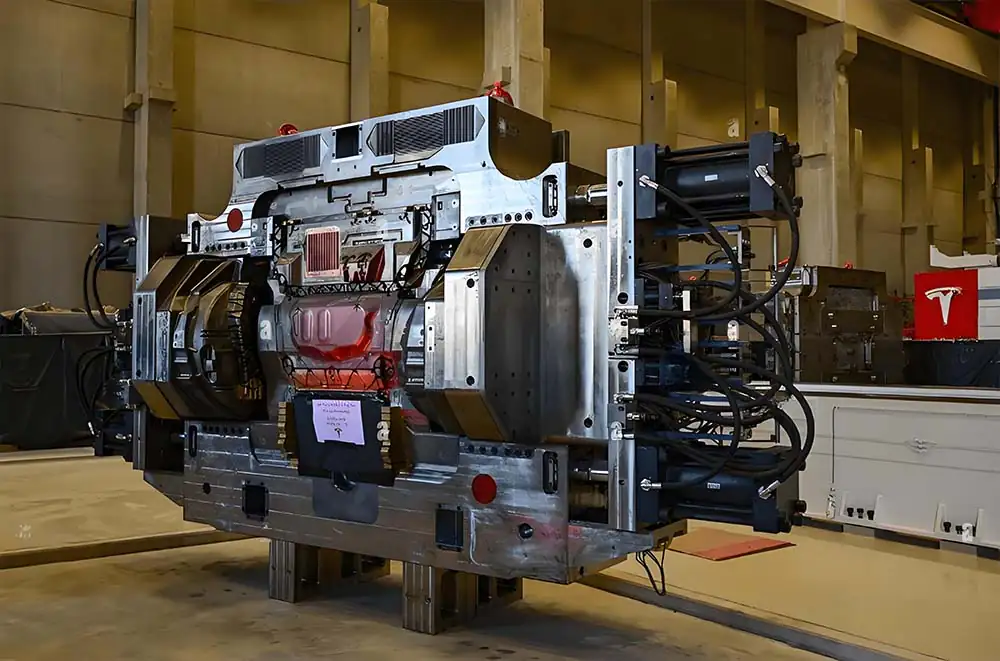
A. Introduction to die-casting molding technology
Pressure casting referred to as die casting, is the use of die casting machine pressure will alloy molten liquid at a certain speed filled with according to certain parts structure and process requirements designed and precision manufacturing mold cavity, and alloy molten liquid to maintain a certain pressure, under the action of the mold cavity, cooling and solidification and molding of a kind of high-efficiency, high-efficiency precision casting technology.
B. Characteristics and application scope of die-casting molding technology
1, the characteristics of die-casting molding technology
High pressure, high speed is die casting liquid or semi-liquid metal filling molding process of the two main characteristics, but also die casting molding technology and other casting method is the most fundamental difference.
2、The application scope of die-casting molding technology
Die casting technology is one of the most advanced metal forming methods, and is an effective way to realize less chips and no chips. At present, the alloy used for die casting is no longer only limited to zinc, aluminum, magnesium and copper alloys, but gradually expanded to cast iron and cast steel and other iron alloys to produce die castings.
C. Development trend of die-casting molding technology
Due to the use of die-casting molding technology, the enterprise has its positive and obvious economic benefits. Future die-casting molding
The technology is moving in the direction of:
(1), die-casting molding technology to the intelligent direction.
(2) Research and development of new materials for die-casting to meet the needs of industrial technological progress.
(3) Research and development of new die-casting equipment to improve automation.
(4) Development of new detection technologies.
(5) Development of new die-casting technology, improve and enhance the level of die-casting technology.
(6), improve die-casting mold life, reduce production costs to solve the problem of ferrous metal die-casting gradually expanded to cast iron and cast steel and other iron alloys to produce die-castings.
Die Casting Mold Design
A. Overview of die casting mold design
- Die casting, die casting mold, die casting machine, die casting alloy through the die casting process parameters of the interlinked coordination, common completion of die casting die casting molding process. Die casting mold in die casting production process is as follows:
- ①.Determine the pouring system, especially the position of the inner gate and the direction of infusion and the position of the overflow system, which together determine the filling conditions of the molten metal and the molding condition;
- ②, die-casting mold is the die casting of the replica, determines the shape and precision of the die casting;
- ③, the quality of the mold forming surface directly affects the surface quality of the die casting and the size of the mold release resistance
- ④, after the die-casting molding, to ensure that the die-castings smoothly from the die-casting mold, and push out the mold body, there should be no changes in the
- The occurrence of shapes, breakages, etc;
- ⑤. The mold has the strength and rigidity to withstand the impact of the injection force and the speed of the inner gate on the mold;
- (vi) Control and regulate the heat exchange and heat balance of the mold during the die casting process;
- (vii) Maximize the molding efficiency of the die-casting machine.
B. Basic principles of die-casting mold design
(1), fully understand the use of die casting and other structural parts of the assembly relationship, and according to the structural characteristics of die casting, the use of performance, in the design of the mold to distinguish between the main and secondary, highlighting the focus of the mold structure as well as the combination of the mold processing process, reasonable choice of mold parting surface, the number of cavities and the layout of the form of die casting form of launching and lateral demolding form.
(2), to understand the actual processing capacity of the site mold, such as the existing equipment and can collaborate with the unit's equipment, as well as the operator's technical level, combined with the actual design of the mold structure form in line with the processing capacity of the site.
(3), the mold should be adapted to the die-casting production of the various process requirements, choose in line with the die-casting process requirements of the pouring system and overflow system, especially the location of the inner gate, the inner gate speed and the direction of the liquid flow, should make the liquid metal flow smoothly and smoothly, and orderly discharge of the cavity gas, in order to achieve a good filling effect and to avoid the generation of defects in die-casting.
(4), under the premise of ensuring stable quality of die castings and safe production, die casting molds should have:
①, simple structure, advanced and reasonable, accurate and reliable operation, and reduced operation procedures.
②, easy to operate, safe and quick, easy to dismantle wearing parts, easy maintenance, low manufacturing cost.
(iii) Higher die-casting efficiency, fast mold filling, fast mold opening, flexible and reliable demolding mechanism and high degree of automation.
(5), mold structural parts should meet the requirements of the machining process and heat treatment process. Selection of appropriate materials, especially the molding parts and other parts in direct contact with the liquid metal, should be selected high-quality heat-resistant steel, and hardening treatment, so that it has sufficient resistance to thermal deformation, fatigue strength and hardness and other comprehensive mechanical properties, as well as corrosion resistance.
(6), should give full consideration to the mold temperature changes on the relative sliding parts of the fit accuracy brought about by the impact.
(7), mold design should be based on the feasibility of the economy for comprehensive consideration.
①, the overall structure of the mold is to strive for simple, practical, comprehensive and inexpensive.
②, should be selected economic, practical size fit accuracy.
(iii) Pay attention to reduce the consumption of residual material of casting system.
In addition to the basic requirements of normal design, special consideration should be given:
1. Adopt reasonable and advanced simple structure to make the workpiece accurate and reliable, and the rigidity of the structure is good, i.e., the mold has enough thickness to ensure that it has enough rigidity to prevent the mold from deformation and cracking. At the same time, we should also consider that the mold is easy to dismantle and replace, which is conducive to the
Extend the life of the mold;
2. The parts on the mold should meet the requirements of machining process and heat treatment process. Try to avoid or reduce sharp corners and thin walls to facilitate subsequent heat treatment and prevent stress concentration. If the structure can not avoid sharp corners, should be in the roughing to reserve enough R angle, heat treatment after machining in place to avoid the risk of heat treatment cracking.
3. Largedie casting mold(The projected area of the parting surface is more than 1 square meter), should use the square guide pillar guidance system, in order to avoid the big difference between the dynamic and fixed molds due to thermal expansion, resulting in the guiding accuracy decline;
4, for the design of large complex die-casting mold pouring system and exhaust system and cooling system, it is best to do flow analysis and heat balance analysis. This arrangement of runner system (straight sprue, cross sprue, inner gate) and constant temperature preheating system location, angle size, quantity, etc. will do reasonable layout; As we all know, the pouring system is the liquid metal from the pressure chamber into the cavity, it is closely related with the liquid metal into the cavity parts, direction, flow state, and can adjust the filling speed, filling time, cavity temperature and other filling conditions. In die casting production, pouring system on die casting quality, die casting operation efficiency, mold life (high temperature, high pressure, high speed liquid metal on mold cavity wall scouring, corrosion, etc.), die casting edge and clean up, etc. also have significant impact, visible pouring system
The design and its importance;
5. Inner gate design considerations:
The high temperature metal liquid entering the cavity from the inner gate should not enter the wall and core of the dynamic fixed model positively, in order to prevent the cavity from early erosion, mold sticking and cracking phenomenon; when using multiple strands of the inner gate, it is necessary to consider the prevention of metal liquid entering the cavity from several ways to converge, and the impact of each other to produce vortex, wrapped in gas and oxidation of the slag and other defects; the choice of the thickness of the inner gate is generally based on empirical data, and it is recommended to meet the conditions of mold filling. Under the condition of filling type, try to choose bigger, to avoid the impact of too large compression and injection speed, causing mold erosion, mold sticking, pitting and cracking in the early stage;
6. Design of overflow and exhaust tanks:
The role of the overflow channel is to accumulate the first into the cavity of the cooling liquid metal and wrapped with gas liquid metal, as well as regulating the temperature of the mold parts, improve the thermal balance of the mold, is conducive to prolonging the service life of the mold. Generally located at the end of the liquid metal process, set up a suitable overflow tank can improve filling conditions, improve the quality of castings. The exhaust groove is used to discharge the air and the gas generated by the volatilization of the paint from the cavity, and the location of its setting is related to the location of the inner gate and the product structure. In order to make the cavity gas injection as far as possible by the die casting of liquid metal discharge, will be set in the last part of the liquid metal filling exhaust tank. The exhaust tank is generally combined with the overflow tank, arranged at the back end of the overflow tank, in order to strengthen the overflow and exhaust effect.
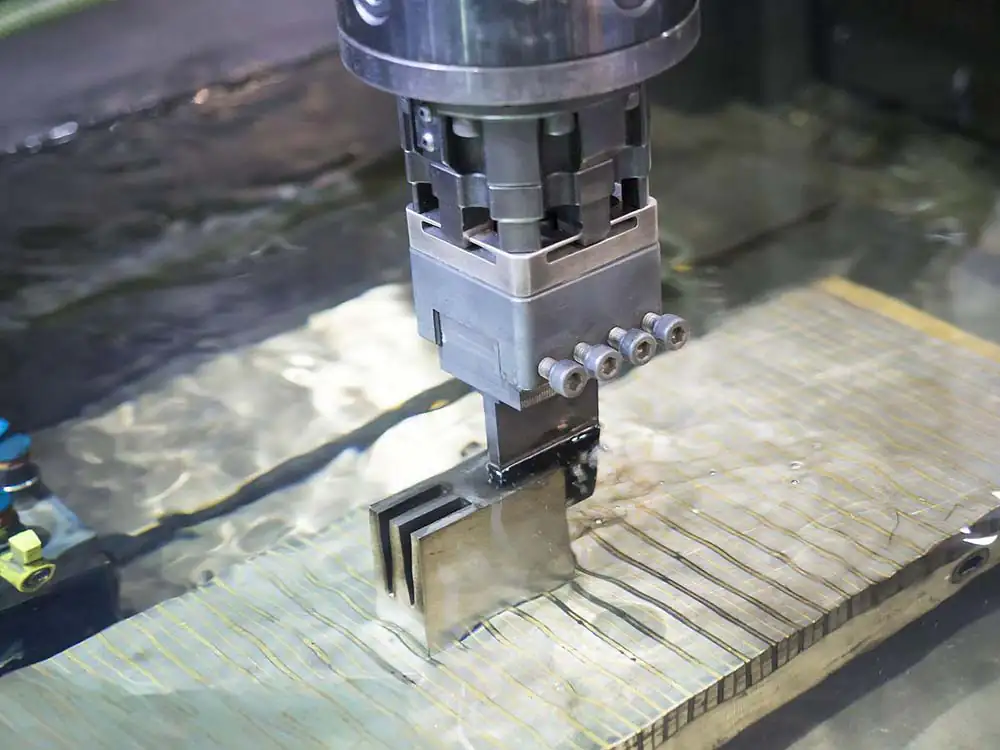

The effect of machining on mold failure
As we all know, die-casting mold manufacturing cycle is long, complex machining, involving turning, grinding, milling, drilling, planingmachiningand electric discharge machining (wire cutting, EDM) and other processes. Its processing quality, especially the surface of the processing quality in the mold manufacturing process and the subsequent use of the process, will significantly affect the mold's fracture resistance, fatigue strength, thermal fatigue resistance and abrasion resistance, corrosion resistance and so on. A slight error in the processing process may cause early failure of the mold. For example, cracking and thermal cracking arealuminumCommon failure phenomenon of die casting mold, it is the mold surface thermal fatigue, stress, low strength and surface roughness caused by.
1, the impact of cutting processing
Module in the machining cutting process, due to the destruction of the original balance of the workpiece substrate, will produce stress, these internal stresses reduce the total strength of the module surface, resulting in the lack of thermal fatigue strength, which will produce cracks or cracks in the corners and small radius arc transition. Therefore, sharp corners should be avoided as much as possible. Sharp corners and machining cuts can significantly cause stress concentration, unless there are special requirements, otherwise, should avoid sharp corners, and make the corner of the arc radius of curvature is fully enlarged, the purpose is to avoid or reduce stress concentration. For example: the arc radius R from 1mm to 5mm, the maximum internal stress is reduced by about 40%, greatly improving the toughness of the mold. When the module arc radius from 2mm to 20mm, the impact toughness can be increased by 4 times. Similarly, the size of the mold surface roughness on the mold life also has a greater impact. Such as the existence of obvious knife marks, cracks, cuts, etc., these processing defects will cause stress concentration, become the root cause of cracks. Therefore, to ensure that the mold surface roughness requirements, the cavity surface should be ground and polished to remove cut marks and other defects. Cooling water hole drilling, if the two-way drilling, misalignment, will cause early cracking in the place, water leakage. Mold embryo cutting allowance is not enough, after forging and annealing of the mold embryo, or mold embryo, core, after processing in the air furnace heating and quenching, there is generally a certain thickness of the decarburization layer, cutting process must be decarburized layer all removed. Otherwise, the residual decarburization layer in the use of the mold, will reduce the thermal fatigue resistance of the mold surface, resulting in cracking of the part.
2. Effect of grinding process:
After heat treatment of die casting molds, the following problems may occur when grinding (including clamping and wheel grinding):
A. Cracking or cracking occurs, which is due to the grinding wheel is too hard, the feed amount is large, the grinding speed is fast, the grinding stress is too large, the cooling is insufficient or the coolant is not properly selected. By the hard grinding wheel caused by the frictional heat generated by the tensile stress is greater than the fracture toughness of the material, cracking will occur;
B. Grinding burns, surface softening. Softened surface in contact with molten die-casting metal, because of its relatively low strength, and thermal fatigue strength is also insufficient, easily lead to cracking, erosion and pitting.
C, grinding stress. Grinding of the mold surface grinding stress, reducing the strength of the mold surface and thermal fatigue resistance, will lead to cracks or cracks in the mold bit corners and small R arc transition, it can be lower than the tempering temperature 20 ~ 30 ℃ temperature for a tempering treatment to achieve the purpose of eliminating stress.
3. Effects of discharge processing
A. Produces a hardened bright white layer
Electrical discharge machining (EDM and wire EDM) of mold cavities is generally carried out after the mold is quenched to ensure the accuracy of the mold. During processing, due to the high temperatures generated instantaneously by a discharge (temperatures up to thousands of degrees Celsius, or even tens of thousands of degrees Celsius), the metal on the surface of the mold rapidly melts, vaporizes, and evaporates. Application of coolant rapid cooling results, from the surface in order: re-solidification layer (thickness of 0.2mm when rough hitting, fine hitting up to 0.01mm or so), and then quenching hardened layer (its thickness is generally within 0.05mm, the most surface side of the overheated quenching organization, brittle and high crack sensitivity), high temperature tempering softened layer and the normal matrix organization. Inside this hardened layer, especially in the re-solidification layer produces many fine cracks, cracks and even extend to the re-quenched hardened layer (often referred to as the bright white layer or metamorphic layer). Its presence can cause accidents such as early cracking or crazing of the mold. (For example, automobile clutch housing, gearbox body mold inserts are often this situation). Therefore, manual grinding, chemical grinding or electrolytic grinding should be used to fully eliminate this deformation layer is very necessary.
B, EDM surface roughness and fatigue strength of the relationship between the electric discharge machining of the electrical gauge parameters, electrode materials, compared with machining, its fatigue strength is much lower. Rough hitting, in the pulse width of 1050μ s when its fatigue strength is about 60% for machining.
C. Protective measures
Regardless of the depth of the white layer of discharge processing, for the poor working conditions of die-casting molds, this white layer must be eliminated (grinding); adjust the discharge process parameters, preferably coarse, fine two-stage discharge processing as far as possible to use high-frequency, small-current process parameters, control the white layer of 0.01mm or so; discharge processing, in addition to sanding to remove the white layer, but also must be immediately carried out for a sufficiently long period of time for the secondary Tempering temperature is usually higher than the final tempering temperature. Tempering temperature is usually lower than the final tempering temperature of 20 ~ 30 ℃ or 30 ~ 50 ℃, in order to fully eliminate the tensile stress on the surface, improve the tempering stability of the re-quenched layer, reduce brittleness.
In general, the defects of cutting, grinding and electric discharge machining on the surface of the mold will reduce the quality of the surface of the mold causing stress concentration. For the die-casting mold in high temperature and high pressure working condition, bear the role of alternating thermal stress and alternating mechanical stress, the mold surface is easy to produce cracking and cracking and corrosion, make the mold early failure. (Of course, there are also affected by steel quality, design, heat treatment, use, maintenance and many other factors). All of these deserve the great attention of mold design engineers, technical craftsmen, production operators and quality inspectors. Put forward reasonable mold surface quality requirements, try to avoid sharp corners of the parts and small radius arc transition connection and obvious knife marks, control the electrical discharge machining of the electrical gauge parameters, to eliminate the white layer and so on. To develop the roughness acceptance standards for cutting, electrical discharge machining and clamp grinding, and strictly implement the inspection system for each process. This will effectively avoid early failure of the mold caused by improper processing and improve the service life of the mold.
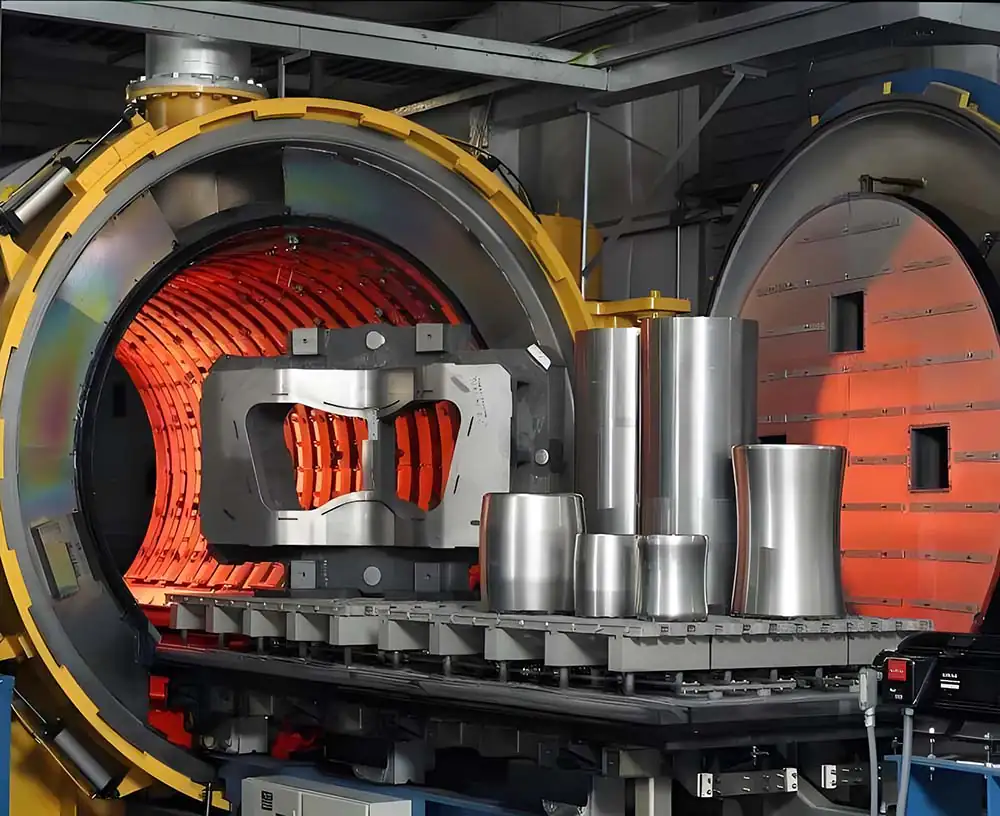
Precautions for heat treatment of die casting molds:
Heat treatment for die-casting mold service life has a greater impact, according to relevant information, due to improper heat treatment, caused by die-casting mold early failure accounted for the whole die-casting mold accident 44% or so. Steel quenching stress, in fact, is the cooling process of thermal stress and phase change when the organization of the superposition of stress results, steel quenched in high stress low toughness state, with high hardness and strength, more brittle, in fact, can not be used. And quenching stress is the cause of deformation cracking, and lead to fatigue strength impact toughness reduction. For this reason, steel must be tempered after quenching to remove stress. Stabilize the organization and improve toughness.
1、 Stress relief annealing treatment before mold quenching
As the mold machining to produce greater internal stress, in order to prevent the heat treatment with the internal stress generated by the iteration, causing mold deformation and cracking, so the mold is required after machining, quenching before a stress relief annealing treatment. Annealing temperature 600 ~ 650 ℃, insulation time in accordance with the thickness of each 25mm, insulation 1 hour calculation, insulation with the furnace cooling to 300 ℃ (also cold to 500 ℃) out of the air-cooled.
2, the development of a reasonable heat treatment process
A. The quenching process adopts multi-stage preheating and strict control of the heating rate 1.2343/44 type steel belongs to medium carbon high alloy steel, its thermal conductivity is relatively poor compared with low alloy steel. Therefore, the quenching heating should adopt multi-stage preheating (2 to 3 stages), for 300℃, 650℃, 850℃ preheating, the purpose is to make the temperature of the workpiece heart and surface tend to be balanced, in order to reduce the thermal stress generated by the temperature difference. At the same time its heating rate should be implemented slowly heating principle (100 to 200 ℃ / h), in order to reduce the thermal stress generated during the heating process. In the high-temperature heating stage can be used faster heating speed (10 ~ 15 ℃ / h) to shorten the high-temperature heating time to prevent grain coarsening;
B. Preventing overheating of workpieces
If the heating stage temperature exceeds the normal quenching temperature (including meter failure or workpiece placement close to the heating element, etc. caused by), with the increase in quenching temperature, holding time extension, grain coarsening in general, the organization of brittleness increases, the increase in residual austenite, the transformation of globular carbides into polygonal carbides, and there is a mesh organization appears, the mold in the use of the process is prone to cracking;
C. Selection of quenching heating medium and cooling medium
Today's world for large and complex precision molds and more vacuum or protective atmosphere heat treatment to prevent mold surface oxidation decarburization, especially vacuum high-pressure air-cooled quenching process is widely used. However, it should be noted that the air cooling rate can not be too low, that requires the nitrogen pressure size is sufficient, usually requires the workpiece from the quenching temperature (1020 ~ 1050 ℃) cold to 538 ℃ in the process of its surface cooling rate of greater than or equal to 28 ℃ / min, there are also requirements for the workpiece cooling rate of greater than or equal to the heart of 28 ℃ / min. If the temperature range, the cooling rate is too slow, the quenching of its microstructure will have carbides or other transformation products precipitated along the grain boundaries, thereby reducing the toughness of steel, increasing brittleness, premature cracking in the process. In addition to the conditions, for particularly complex large die-casting molds can be used graded isothermal quenching, can effectively reduce the mold deformation and avoid cracking.
D. Tempering process
Temper in time after quenching. Workpiece quenching after cooling to 90 ~ 70 ℃ should be tempered immediately, because the workpiece after quenching is in high stress, low plasticity state, easy to cause cracking; Tempering to be sufficient. Large complex die-casting mold after quenching, usually three tempering, each tempering time according to the effective thickness of the workpiece every 25mm insulation 1 hour calculation, but not less than 4 hours. The purpose is to reduce the organization transformation stress and stabilize the size.
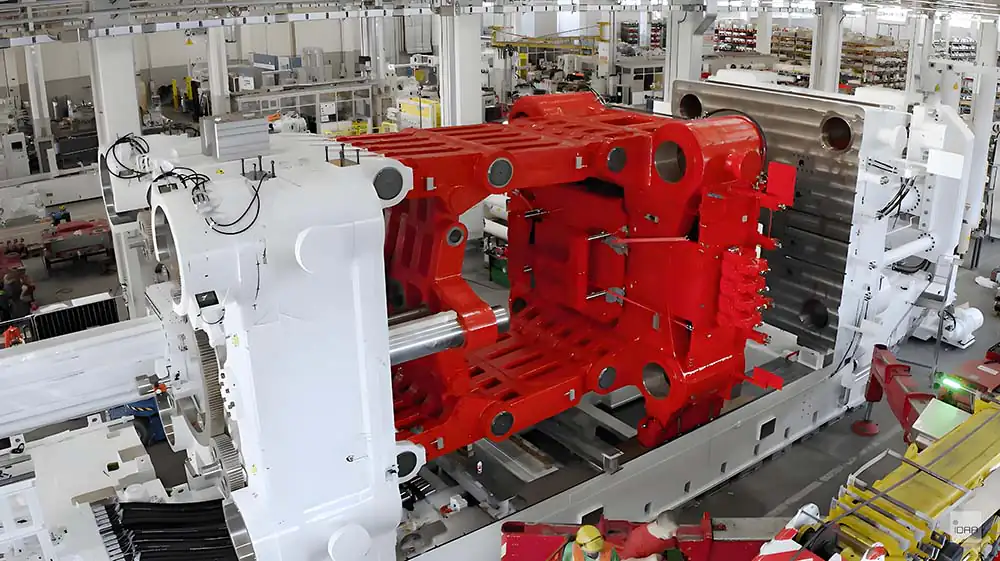
Die casting mold die casting production and maintenance considerations
1、 Good preheating of the mold
Mold assembly after the trial mold or normal production, must preheat the mold and mold temperature should be uniform. Aluminum and magnesium alloy die-casting mold preheating temperature is recommended at 250 ~ 320 ℃, the best use of mold temperature machine preheating; mold preheating to 300 ℃, its impact toughness increase very quickly, but when the mold temperature is lower than 200 ℃, the impact toughness of the material is reduced a lot, brittleness increase; after good preheating of the mold, its thermal conductivity is higher than the mold without a good preheating of the mold is close to 20%; mold pouring temperature and mold Surface temperature (preheating temperature) the greater the difference, the greater the thermal stress, the more likely to cause thermal fatigue and cracking. Japan die casting association editorial information, mold temperature from 250 ℃ to 350 ℃, that is, pouring temperature and mold surface temperature difference reduce 100 ℃, the mold life can be increased almost 10 times.
2、 Formulate the correct casting process
The pouring temperature should be reasonable, not too high. Otherwise the pouring temperature is too high, although the fluidity is better, but the casting condensation time is long, easy to produce shrinkage holes, air holes, easy to reduce the mold surface hardness, appear sticky mold, produce crack. Adjust the clamping force of the die casting machine, so that the mold force is uniform. Correctly select (or adjust) filling speed and filling pressure. Filling speed (ejection speed) is too high will increase the cavity surface due to erosion and sticking mold damage chances, too low filling speed, although conducive to gas discharge, but will make the casting mechanical properties and surface quality deterioration. Similarly, the increase in filling pressure will also increase the nozzle filling speed. In short, to adjust a moderate value.
3、 Turn off the cooling water during production
When interrupting the die casting pouring operation, remember to turn off the cooling water, so as not to make the mold temperature drop too much, so that when resuming the pouring operation, affecting the casting quality and mold life.
4、 Selection of suitable mold release agent and the correct spraying method
Die casting to be sprayed in the metal solution contact cavity surface, its main role is to avoid the metal liquid adhesion in the cavity surface and ensure that the casting and the wall separation, prolong the life of the mold. Mold release agent has water, oil, in recent years, but also developed a powder and granular mold release agent. Requirements: mold release agent can not have a negative impact on the surface quality of the casting, no smell of smoke occurs, and shall not leave a residue. Mold release agent concentration should be appropriate, often stirring, never let it precipitate, otherwise the mold cavity will be extremely cold caused by thermal fatigue cracking. Spraying amount should be less, spraying should be uniform, the formation of the film should be thin. Spraying too much too thick will cause castings loose, slag, blistering, porosity and other defects. If the spraying effect of water-based mold release agent is not good, you should choose oil-based mold release agent or powder-based mold release agent. However, it should be used under vacuum. The casting demolding is fast, high productivity, good quality, and the mold produces less thermal stress, which is conducive to prolonging the service life of the mold.
5. Ensure that the casting of aluminum alloy quality assurance of aluminum alloy composition;
Aluminum alloy melting and holding tank must be separated. Central melting should strictly control the content of gases such as oxides, absolutely avoid the scrap and back to the furnace material directly into the holding furnace, otherwise it will contaminate the metal solution, not only seriously reduce the quality of the casting, it will be more likely to cause sticking mold and corrosion of the mold. Aluminum alloy solution Fe content should be controlled between 0.7 ~ 1.3%, if less than 0.7% is easy to cause the phenomenon of sticking to the mold, if greater than 1.3% will form a metal compound hard point, resulting in erosion.
6, establish a good mold maintenance system, so that the mold is in good working condition:
A, timely cleaning and cleaning molds, remove cavity residues and flying edge; B, replacement or repair of damaged parts; C, regular stress relieving treatment of the mold: the first stress relieving treatment for the initial commissioning of the mold to use about 2000 ~ 5000 die times; the second stress relieving treatment for the use of 10,000 ~ 20,000 die times; the rest of the each stress relieving treatment intervals, the maximum can not be more than 15,000 die times. D. After using the mold for a period of time, the hardness of the surface of the mold will be reduced, and the phenomenon of sticking to the mold will occur, the surface of the mold should be ground smooth, and a nitriding treatment should be carried out with a thickness of nitriding layer of 0.08-0.12mm, or nitriding + oxidizing composite treatment, which will effectively improve the service life of the mold.


















