High quality parts
With 15 years of manufacturing experience, HEXIN offers precision die casting with comprehensive quality checks at all stages: before production, during production, first article inspection and before delivery.
Fast product delivery
HEXIN's network of die cast manufacturers in China ensures efficient and rapid production. Our capabilities include state-of-the-art automation facilities to support complex customized projects.
Die Casting Specialist
As experts in customized die casting solutions, we can increase product durability and reduce costs. Our advanced technology and machinery ensures that every part is high quality, functional and aesthetically pleasing.
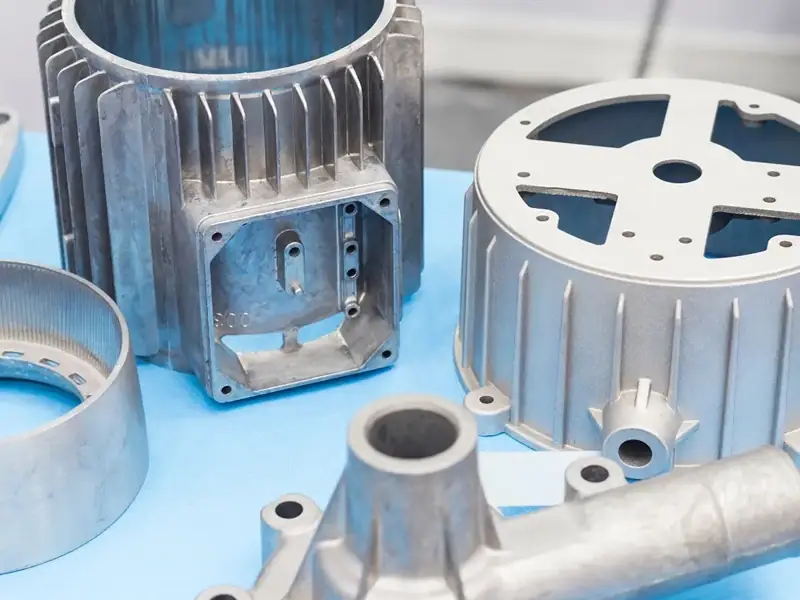
What is Die Casting
Die casting is through the mold molding metal parts process, mainly divided into high-pressure casting (high-pressure rapid prototyping, suitable for complex precision parts and thin-walled structure), low-pressure casting (low-pressure slow filling, specializing in high mechanical properties and hollow parts) and gravity casting (natural gravity casting, suitable for large and simple). parts). Based on the precision die casting equipment and customized process, Hersin Moulding provides the whole process service from mould design to post-processing for the needs of new energy vehicles, electronic radiators, etc., taking into account the high precision, high denseness and surface finish of the parts, and helps customers optimize the production efficiency and performance of the products, and realizes the seamless connection from prototype development to mass manufacturing.
At Hersin, our team of experts scrutinizes each die casting project to ensure that our approach meets your specific requirements. We prioritize the optimization of our production process to ensure that each component meets high standards of durability and aesthetics. By focusing on advanced casting techniques and utilizing precision die casting machines, we can help you achieve excellence in both function and appearance, ultimately increasing the overall value of your product.
Application areas of die castingDie casting is a high-precision, high-efficiency metal casting process that is widely used in a number of industries because of its ability to produce components with precise dimensions and consistent quality. The following are the main application areas of the die casting process:

High pressure die casting advantages and disadvantagesThe high-pressure die casting process offers several unique advantages in the manufacture of metal parts, making it the technology of choice for complex precision components in the automotive, consumer electronics, and appliance industries:
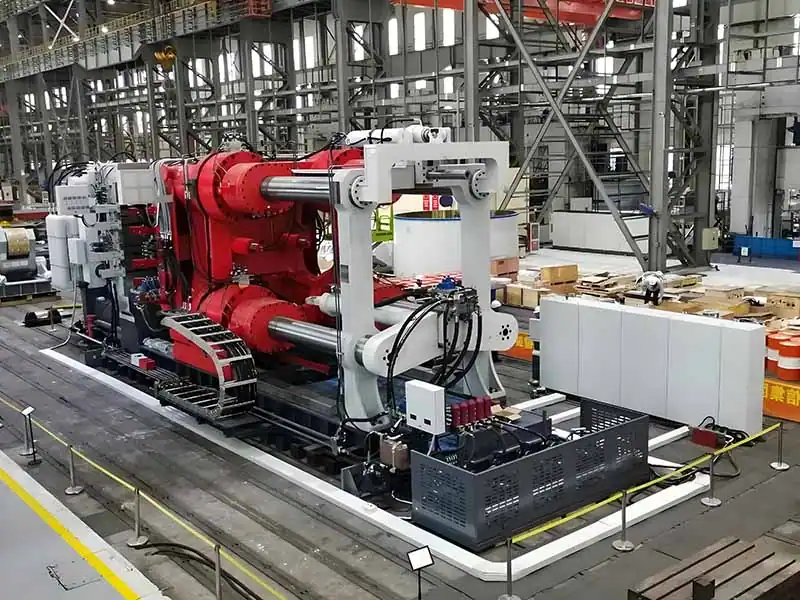
Advantages and disadvantages of low pressure die castingThe low-pressure die casting process has a number of unique advantages in the manufacture of metal parts, making it the technology of choice for components with high mechanical properties in the automotive, aerospace, and industrial equipment sectors:
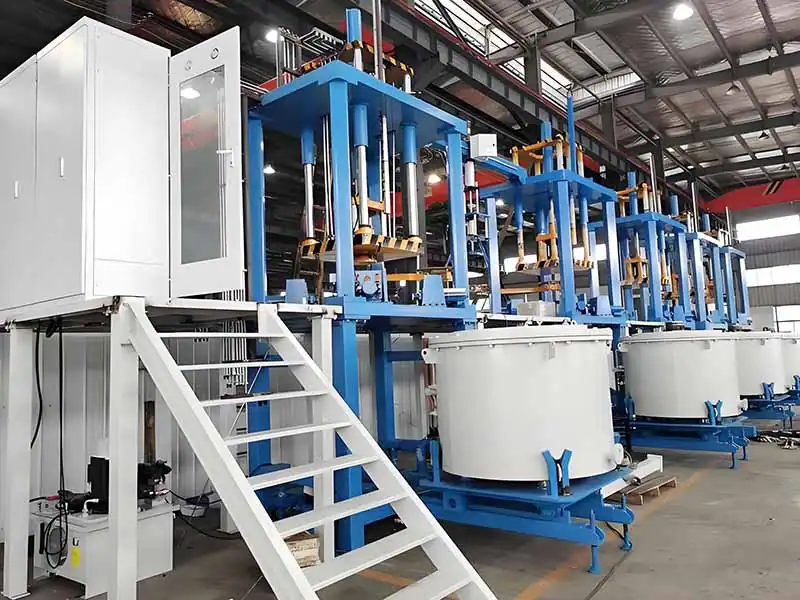

Gravity Die Casting Advantages and DisadvantagesThe gravity die casting process has a number of unique advantages when it comes to manufacturing metal parts, making it the technology of choice for large, thick-walled parts in the heavy machinery, agricultural equipment, and construction industries:
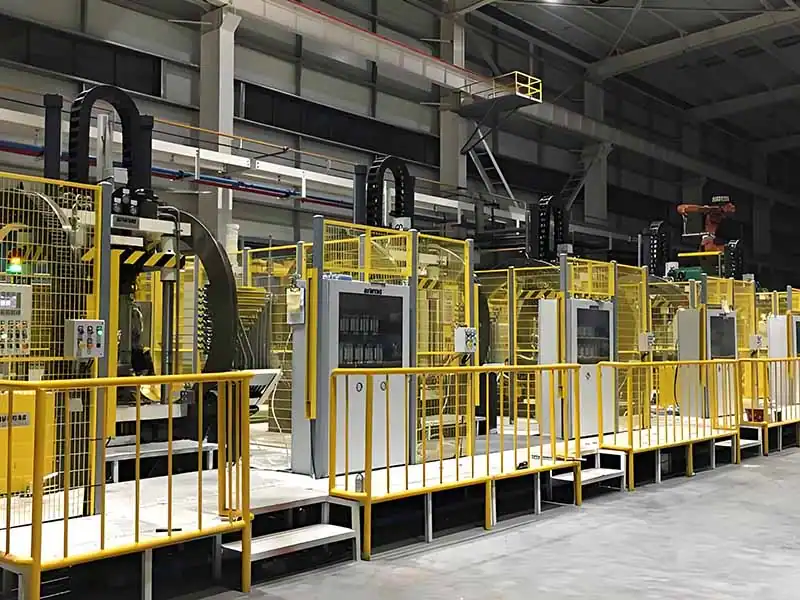

What is the die casting process?
Die casting is a casting process in which molten metal (e.g. aluminum, zinc, magnesium alloys) is injected into a precision mold under high pressure. The process is capable of producing parts with complex shapes and precise dimensions, and is widely used in the automotive, electronics, and home appliance industries. Through high-pressure injection, the molten metal fills the mold, and after cooling, the part is formed with good surface quality and high strength.
How productive is die casting?
The die casting process is highly productive and suitable for mass production. Once the mold is made, a large number of parts can be produced efficiently. Due to the high pressure injection of molten metal to fill the mold, the parts can be formed in a short period of time, shortening the production cycle, especially suitable for industries with high demand, such as the automotive and electronics industries.
What defects can occur in the die casting process?
The following defects may occur during the die casting process:
- stoma: A cavity formed when gas fails to escape or cools unevenly.
- cold storage: A crack or weak area formed by the failure of the metal to flow and join completely.
- crackles: Cracks caused by improper mold design, uneven cooling or excessive metal stress.
- surface defect: such as scratches, bubbles, etc., which may affect the cosmetic quality of the part.
Can die castings be post-processed?
Yes, die castings usually require some post-processing to further improve dimensional accuracy and surface quality. Common post-processing techniques include:
- machining: Such as milling, turning, etc., for resizing parts and removing burrs or irregular surfaces.
- surface treatment: Such as sandblasting, polishing, anodizing, etc., used to improve the appearance quality and corrosion resistance of parts.
- hot treatment (e.g. of metal): To improve the hardness and strength of a part by annealing, quenching, etc., to meet specific work requirements.
What are the tolerances for die casting?
Tolerances for die casting processes are usually between ±0.1mm and ±0.5mm, with the exact tolerance range depending on the size and shape of the part. Through precise mold design and strict process control, die castings can achieve high dimensional accuracy and are suitable for industrial applications that require high tolerance requirements.
What is the usual lead time for die casting molds?
The lead time for die casting molds is usually 4 to 8 weeks, depending on the complexity of the mold, the choice of material, and the production capacity of the manufacturer. If the mold design is complex or requires multiple adjustments, the lead time may be extended.
What do I need to pay attention to in die casting design?
The following points need to be considered for die casting design:
- Wall thickness uniformity: The wall thickness of the part should be uniform to avoid cold segregation or distortion.
- Rational exhaust design: Design venting holes to expel air and gas to avoid porosity defects.
- Cooling system design: There should be suitable cooling channels inside the mold to ensure uniform cooling of the molten metal and to reduce internal stress and deformation.
- Runner and gate design: Reasonable design of runner and gate system to ensure the smooth flow of metal into the mold to avoid defects.
Why does porosity occur in die casting and how can it be avoided?
Porosity is formed when gas or air is not completely expelled from the molten metal. Common causes include poor exhaust design, excessive metal injection rate, and uneven cooling. Measures to avoid porosity are:
- Improved exhaust design: Ensure that the mold is designed with adequate air vents.
- Control of injection rate: Avoid excessive injection pressures and velocities that result in trapped gas.
- Optimization of casting temperature: Ensure that the molten metal is at the right temperature and avoid overcooling or overheating.





























